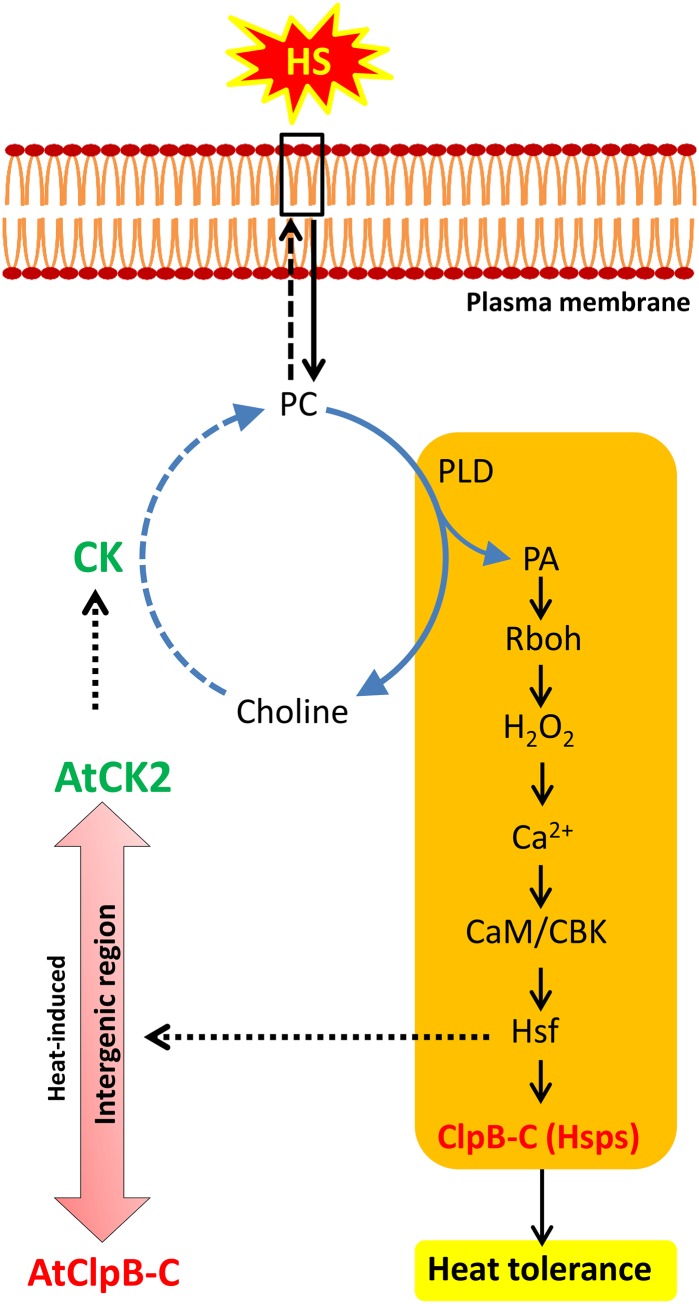
Figure 8.
Model highlighting the possible function and position of heat-induced CK among the key players of the PA-mediated heat-signaling pathway, elicited by the plasma membrane during HS. It is previously shown that heat-induced PA accumulation causes a series of reactions ultimately resulting in induction of Hsps (see text for details). The step-wise components involved in this cascade are shown in the rectangular box. Heat-induced CK might compensate for the loss of PC by actively phosphorylating choline generated by PC breakdown, thereby increasing PC biosynthesis. In the AtClpB-C:AtCK2 divergent pair, CK induction during HS by Hsf may help in generation of the required PC for uninterrupted signaling. The steps in this model indicated by filled arrows are based on published evidence. The dotted arrows represent the hypothesis forwarded in this study. The cycle shown with circular arrows represents the Kennedy pathway for PC biosynthesis. CaM, Calmodulin; CBK, calmodulin binding kinase; PLD, phospholipase D; Rboh, respiratory burst oxidase homolog. [See online article for color version of this figure.]