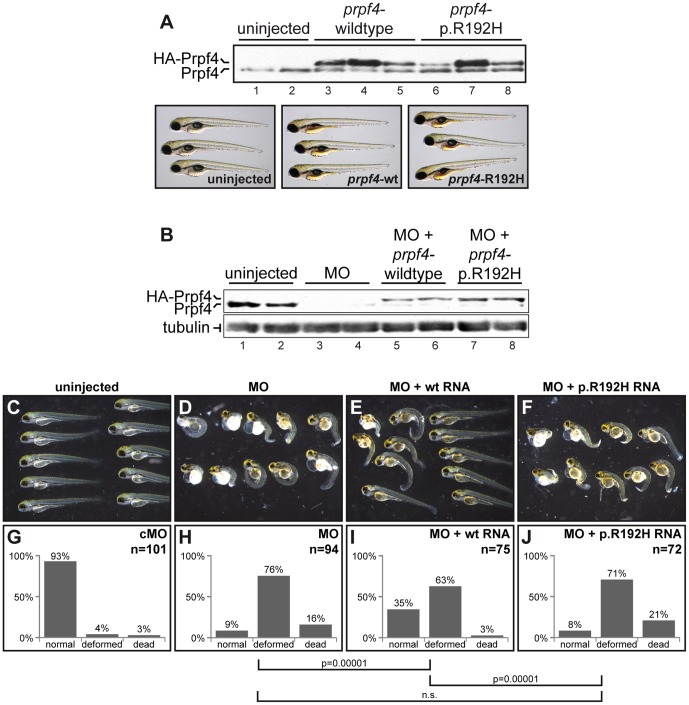
Figure 2. The p.R192H variant leads to a loss of function in vivo.
(A) Expression of zebrafish Prpf4 carrying a mutation corresponding to p.R192H does not have a dominant negative effect. Upper panel: Western blot detection of endogenous Prpf4 and exogenous HA-tagged Prpf4 in embryos injected with RNAs indicated above. Lower panel: No defects in embryonic development were observed upon overexpression of wildtype or p.R192H Prpf4. (B) Western blot showing Prpf4 protein levels in zebrafish injected with the indicated combinations of prpf4 morpholino (MO) and RNA. (C–F) The p.R192H mutant fails to rescue a lethal prpf4 deficiency. Representative selections of 3 days post fertilization (dpf) larvae from embryos injected with the indicated combinations of prpf4 morpholino (MO) and RNA. (G–J) Quantification of normal, deformed and dead animals from four independent rescue experiments. The rescue effect (H vs. I) and the loss of function effect of the p.R192H mutation (I vs. J) were highly significant (Pearson χ2 test; n is the total number of injected animals). Please note that the control experiments (uninjected, MO and MO + wt RNA), but not the characterization of p.R192H, were previously published as part of a larger knockdown study [22]. As the characterization of p.R192H has been performed in the context of this study, we reproduce here the control data for clarity (with permission from Oxford University Press).