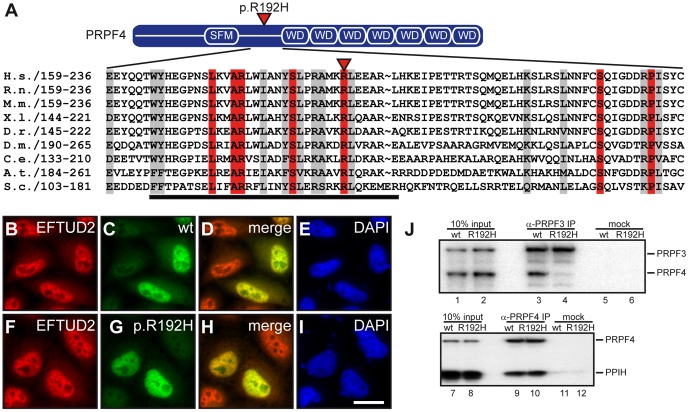
Figure 3. Characterization of the PRPF4 missense variant p.R192H identified in an RP patient.
(A) Domain organization of PRPF4 (upper panel). The p.R192H amino acid exchange is located between the splicing factor motif (SFM) and the WD40 repeat domain (WD). Amino acid sequence alignment revealed a strong conservation of the affected arginine residue across species (lower panel). Identical residues are shown in red; similarity greater than 70% (BLOSUM62) is indicated by a grey box. See table S1 for sequence accession numbers. (B–I) The subcellular localization of PRPF4 is not affected by the p.R192H mutant. Wildtype (B–E) and the p.R192H form of PRPF4 (F–I) were detected in the nuclei of transfected HeLa cells. Both proteins co-localized with EFTUD2 protein in a speckled pattern typical for splicing factors (B, F). Nuclei were control-stained with DAPI (E, I). The scale bar in K is 20 µm and accounts for all images. (J) The p.R192H missense mutant impairs binding to PRPF3. Immunoprecipitation analysis of in vitro translated [35S]-labeled PRPF4-PRPF3 complex (upper panel) using an anti-PRPF3 antibody revealed a significant reduction of co-precipitated p.R192H-PRPF4 (compare lanes 3 and 4). The interaction of PRPF4 to PPIH in contrast, was not affected (compare lanes 9 and 10). Lanes 1, 2, 7 and 8 show 10% of the inputs, lanes 5, 6, 11 and 12 are mock immunoprecipitations.