Figure 4. The arginine residue at position 192 is essential for integration of PRPF4 into snRNPs.
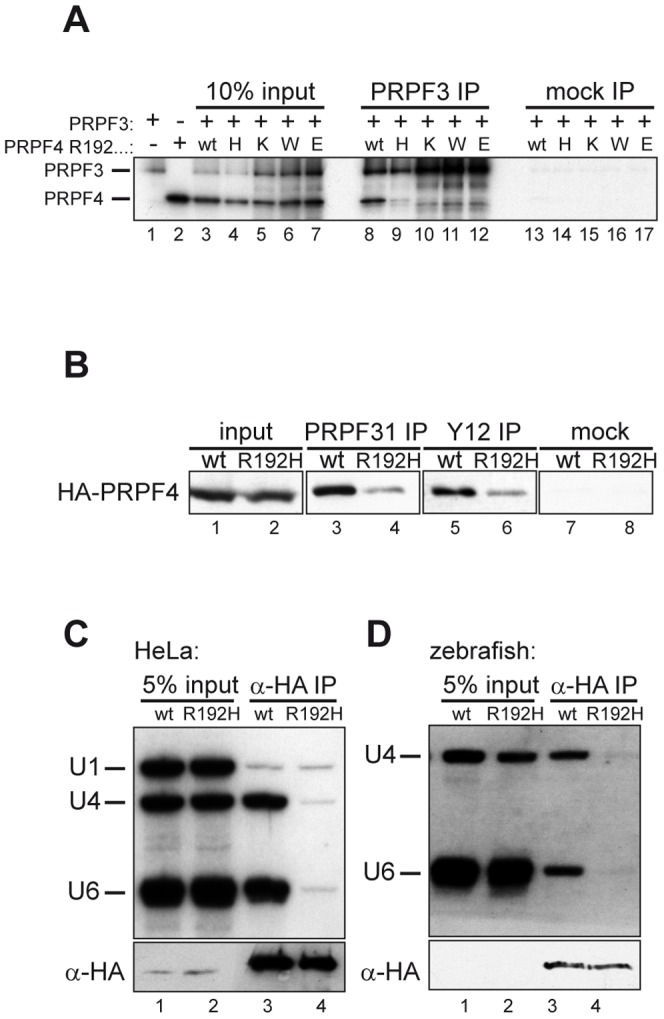
(A) A series of mutants at position 192 was analyzed for binding to PRPF3. Neither lysine (positively charged) nor tryptophan (aromatic) nor glutamate (negatively charged) were tolerated at this position. (B) Reduced co-precipitation of p.R192H PRPF4 with snRNPs. HEK293 cells were transfected with wildtype and mutant HA-PRPF4 and lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-PRPF31 antibody (lanes 3 and 4), anti-Sm-antibody Y12 (lanes 5 and 6) or mock precipitated (lanes 7 and 8). Lanes 1 and 2 show 10% of the input used for the immunoprecipitations. (C) PRPF4 p.R192H fails to associate with U4 and U6 snRNA. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-tagged PRPF4 in either wildtype or p.R192H mutant form. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation was controlled by Western blot (lower panel) and co-precipitated di-snRNP RNAs U4 and U6 were analyzed by Northern blotting (upper panel). U1 snRNA served as a specificity control. (D) snRNA co-immunoprecipitation experiments using zebrafish embryo lysates. Embryos were co-injected with 50 pg wildtype or p.R192H HA-prpf4 mRNA and 0.5 ng prpf4-MO to facilitate snRNP integration of exogenous protein. At 10 hpf, extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitations were analyzed as described in (C).
