Figure 9.
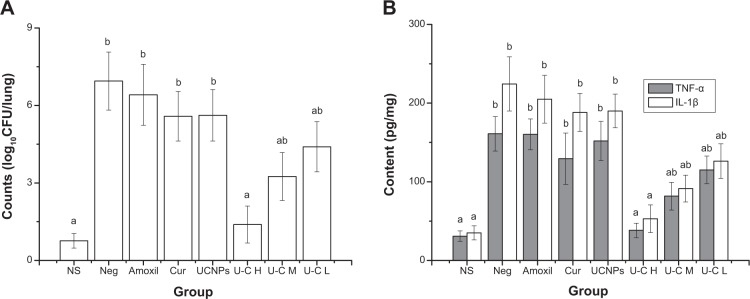
Effects of the treatments on bacterial density (A) and cytokines (B) in lungs of mice. Normal saline (NS), negative (Neg), amoxicillin (Amoxil), curcumin (Cur), upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) 45 mg/kg intravenous (IV); U–C H, U–C M, and U–C L are UCNPs-curcumin with IV injection at high dose (45 mg/kg), middle dose (15 mg/kg), and low dose (5 mg/kg). Mice, except the normal group, were intranasally administered with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (1×106 colony-forming units [CFU]/mL), treated by drugs and 980 nm irradiation (0.5 W/cm2, 30 minutes) on the chest for 3 days, and then euthanized. Lungs were taken for bacterial counting and determination of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation .
Notes: aP<0.01, compared with negative group; bP<0.01, compared with normal group.
