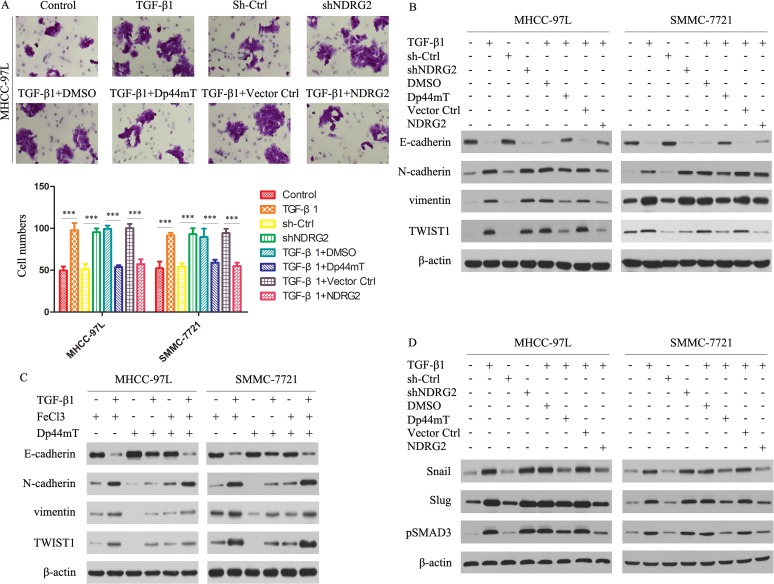
Figure 4. Dp44mT attenuates the TGF-β1-induced EMT in MHCC-97L and SMMC-7721 cells.
(A) Cell invasion experiment results showed TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml) or NDRG2 knockdown significantly enhanced the invasive capacity of MHCC-97L cells, and Dp44mT (10 μM) and NDRG2 overexpression attenuated the TGF-β1/ NDRG2 knockdown induced activation of invasion in MHCC-97L and SMMC-7721 cells. The results represent means ± SD of experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Cells were pretreated in the presence or absence of TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml) for 48 hours and followed by co-incubation with Dp44mT (10 μM) for another 24 h. The expression of indicated proteins were detected by immunoblotting. (C) Iron (FeCl3) inhibits Dp44mT's ability to attenuate the TGF-β1-induced EMT. HCC cells were pre-treated in the presence or absence of TGF-β (5 ng/mL) for 48 h and followed by co-incubation with either: FeCl3 (20 μM), Dp44mT (10 μM) or Dp44mT (10 μM) + FeCl3 (20 μM) for another 24 h. (D) Immunoblotting showed that TGF-β1 or shNDRG2 treatment increases the expression of Snail, Slug and pSMAD3. Dp44mT or NDRG2 overexpression can attenuate the effect of TGF-β1. β-actin was used as the internal control. All assays were done in triplicate.