Figure 3. Accumulation of genomic instability in NPC cells after recurrent EBV BALF3 expression.
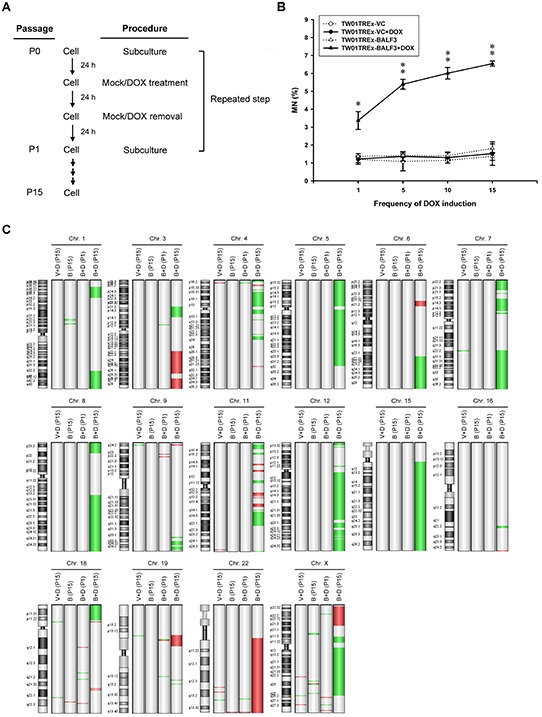
(A) Representative illustration of recurrent EBV BALF3 expression in NPC cells. The recurrent EBV BALF3 expression protocol was as follows. Cells were seeded on a culture plate and incubated for 24 h, followed by mock treatment or treatment with 5 ng/ml DOX for 24 h. After incubation, the culture medium was replaced and incubated for 24 h prior to cell subculture for the next round. These above procedures were defined as one passage (P) and repeated. The cycle was carried out up to 15 rounds. Mock, mock treatment; DOX, doxycycline; P, passage. (B) The cells were harvested at passages 1, 5, 10 and 15 and subjected to micronucleus assay. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations. Student's t test was used to determine the difference between two groups. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, compared to TW01TREx-BALF3 cells without DOX treatment. DOX, doxycycline; MN, micronucleus. (C) The genomic DNA of cells at passages 1 and 15 were extracted and subjected to array CGH and TW01TREx-BALF3 (P1) was used as a common reference. Images were produced by Agilent Genomic Workbench version 7.0.4.0. The location of amplifications and deletions of each group was displayed to the right side of the graph of a chromosome with cytobands. Red and green colors indicate amplification and deletion, respectively. V+D, TW01TREx-VC+DOX; B, TW01TREx-BALF3; B+D, TW01TREx-BALF3+DOX; DOX, doxycycline; P, passage; Chr, chromosome.
