Figure 4. Rer1 interacts primarily with PMP22 mutants retained in the ER.
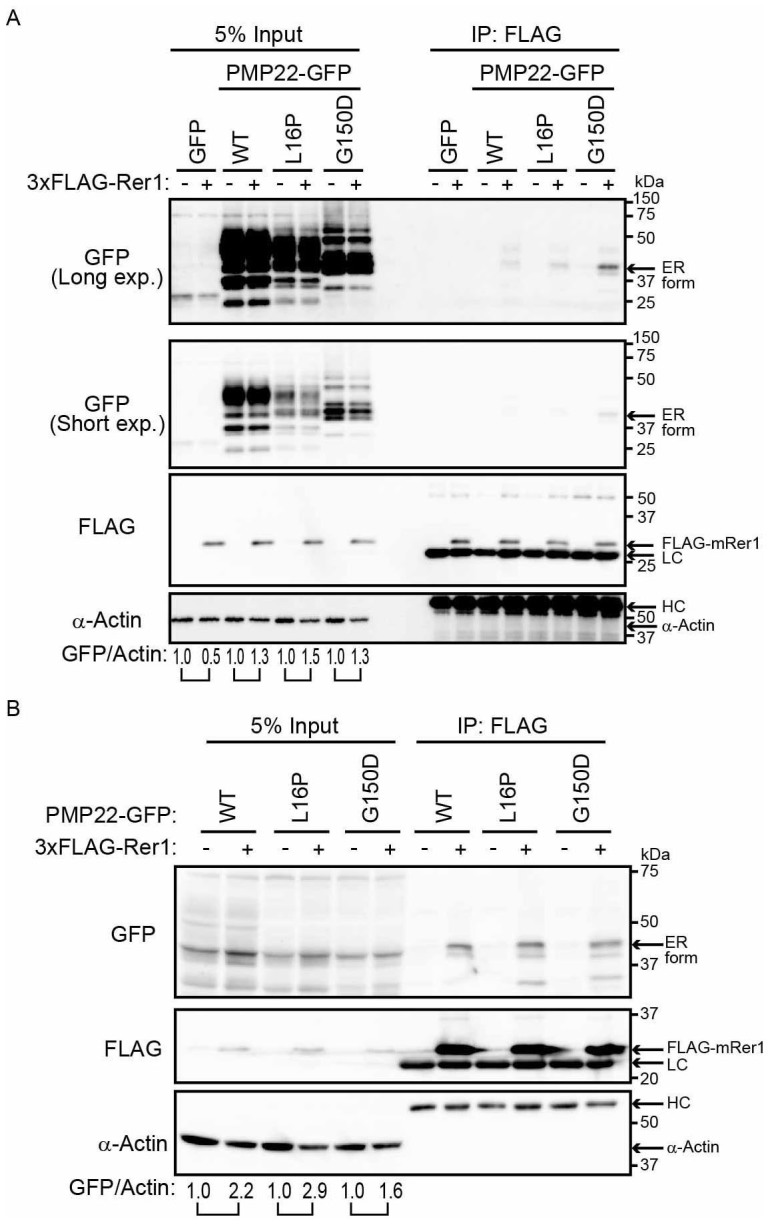
(A) Interaction of PMP22-GFP with FLAG-Rer1. HEK293T cells stably expressing WT or mutant PMP22-GFP were transiently transfected with empty vector (-) or 3xFLAG-mouse Rer1 (+). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with FLAG-M2 agarose beads. The immunoprecipitates (IP) and cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The signal intensities of each PMP22-GFP derivative and α-actin in each cell lysate were quantified using image J software, and the amount of each PMP22-GFP derivative was normalised to the amount of α-actin. To compare the amounts of PMP22-GFP derivatives in mock transfected cells (−) and FLAG-Rer1 transfected cells (+), we calculated the fold changes (GFP/actin) by expressing each normalised value relative to the normalised value obtained with each PMP22-GFP derivative in mock-transfected cells. (B) Interaction between PMP22-GFP and FLAG-Rer1 in cells overexpressing PMP22-GFPs. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the indicated PMP22-GFP mutants, empty vector (−), or 3xFLAG-mouse Rer1 (+). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using FLAG-M2 agarose beads. The precipitates were analysed using western blotting with the indicated antibodies. The immunoglobulin G heavy (HC) and light (LC) chains are indicated. The fold changes (GFP/actin) were analysed as described in panel A. Note that cropped western blots are shown, and full-length images are presented in the supplementary information.
