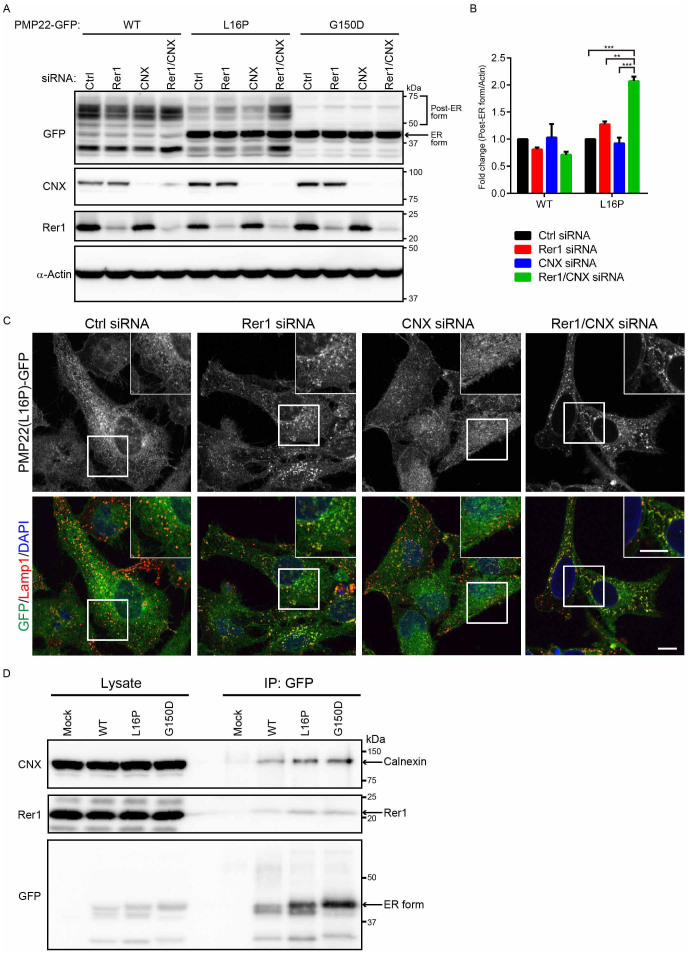
Figure 6. Calnexin and Rer1 mediate the ER retention of PMP22(L16P).
(A) Simultaneous knockdown of Rer1 and calnexin drastically increases the post-ER form of the PMP22(L16P). HeLa cells stably expressing WT or mutant PMP22-GFP were transfected with control or siRNAs against Rer1, calnexin, or both for 3 days. Note that a half amount of siRNA used in Figs. 3 and 5 was used for knockdown of calnexin, Rer1, or both. Lysates prepared from these cells were immunoblotted using anti-GFP (top panel), anti-calnexin (CNX, second panel), anti-Rer1 (third panel), and anti-α-actin (bottom panel) antibodies. (B) The signal intensities of the post-ER form of WT or L16P mutant PMP22 and α-actin were quantified using image J software, and the amount of each post-ER form was normalised to the amount of α-actin. To compare the amounts of the post-ER form in control cells and each knockdown cell, we calculated the fold changes by expressing each normalised value relative to the normalised value obtained with the amount of the post-ER form in control cells. The histogram shows the average values ± SEM from triplicate tests. Two-way ANOVA was used to determine the significance of the differences. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (ANOVA). (C) Simultaneous knockdown of Rer1 and calnexin strongly releases ER-trapped PMP22(L16P) mutant. HeLa cells stably expressing WT or mutant PMP22-GFP were treated with control or siRNA against Rer1, calnexin, or both for 3 days. Then, the fixed cells were observed using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Endogenous Rer1 and calnexin interact with PMP22-GFPs. HEK293T cells were transfected with an empty vector or PMP22-GFP constructs and treated with a chemical crosslinker, DSP. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using an anti-GFP antibody and the blots were probed with the indicated antibodies. Note that cropped western blots are shown, and full-length images are presented in the supplementary information.