Figure 2.
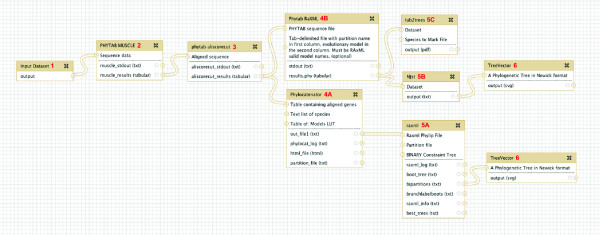
Workflow. Here we show a workflow constructed in Galaxy’s workflow editor. The analysis starts with the input dataset (1), which in this instance would be an unaligned tab-delimited, four-column phytab file. The raw phytab file then gets aligned (2) using phytab-MUSCLE, which will implement a multiple sequence alignment on each gene individually. After alignment, we implement a masking step (3) using phytab-aliscorecut, which will remove ambiguous regions separately from each gene. The data are now ready to be concatenated using phylocatenator (4A), and used to reconstruct a phylogeny with RAxML (5A). Alternatively or simultaneously, the data from step 3 can be used to estimate a separate phylogeny for each gene using phytab-RAxML (4B), which stores all gene trees in tabular format. Subsequently, gene trees can be used to estimate a species tree using NJst (5B), and/or all gene trees can be plotted individually for visual inspection using tab2trees (5C). Finally, any resulting tree file in Newick format can be plotted using TreeVector (6).
