Figure 1.
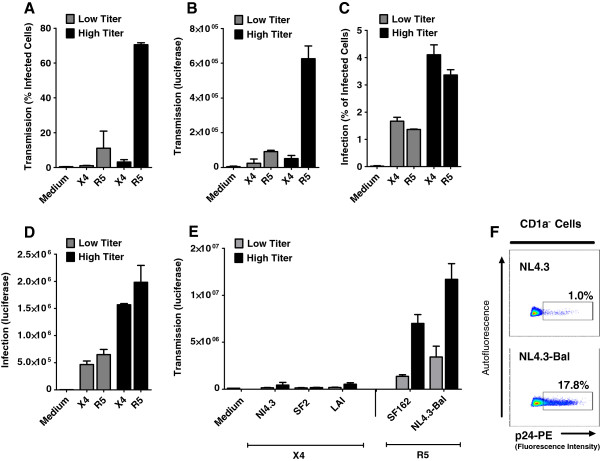
Human primary LCs predominantly transmit R5 HIV-1. (A-B) Human epidermal sheets were pulsed with low (4000 IU or 40 ng HIV-1 p24) or high (20000 IU or 400 ng HIV-1 p24) titers of HIV-1 NL4.3 (X4) or HIV-1 NL4.3-Bal (R5) for 5 hours (A) At day 3, emigrated LCs were cocultured with CCR5 vector-transduced Jurkat (CCR5 Jurkat T cells) and infection of Jurkat cells was measured at day 6 by intracellular p24 staining or GFP expression. T cell-marker CD3 and LC-marker CD1a were used to exclude LCs and LCs-T cells conjugates from analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. (B) Emigrated LCs were cocultured with TZM-bl cells for 2 days and infection was determined by measuring luciferase activity (relative luciferase units [RLU]). Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. (C-D) CCR5 Jurkat T cells (C) and TZM-bl cells (D) were infected with low or high titers of X4 and R5 virus, and infection was determined by intracellular p24 staining or luciferase activity respectively at day 2. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of triplicates. (E) Epidermal sheets were infected with different X4 (HIV-1 SF2, LAI and NL4.3) and R5 viruses (SF162 and HIV-1 NL4.3-Bal). Emigrated LCs were cocultured with TZM-bl cells and infection of TZM-bl cells was determined by luciferase activity. Error bars represent the mean ± standard errors of the mean (SEM) of at least 3 independent experiments. (F) Vaginal LCs were exposed to X4 and R5 HIV-1 and after 3 days were co-cultured with CCR5 Jurkat T cells. Transmission was determined by measuring infection of CCR5 Jurkat T cells by intracellular p24 staining after 3 days. Dotplots represents two independent experiments/donors.
