Figure 3.
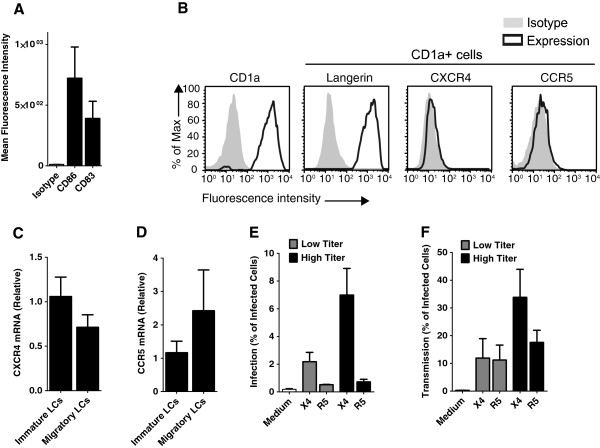
Activated LCs efficiently transmit X4 HIV-1 variants. (A) Migratory LCs were analysed for expression of CD83 and CD86 by flow cytometry. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 different donors. (B) Surface expression of HIV-1 coreceptors on migratory LCs was determined by CCR5 and CXCR4 staining in combination of LC-markers CD1a and langerin by flow cytometry. (C-D) Immature LCs and migratory LCs were isolated and harvested and mRNA expression of CCR5 (C) and CXCR4 (D) was measured by real-time qPCR. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 donors. (E) Migratory LCs were infected with different titers of NL4.3 (X4) and NL4.3-Bal (R5) HIV-1. After 3 days infection of LCs was determined by intracellular HIV-1 p24 staining or GFP expression in combination with LC-marker CD1a by flow cytometric analysis. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. (F) Migratory LCs were pulsed with X4 or R5 HIV-1 strains and after 3 days, cocultured with CCR5 Jurkat T cells for additional 3 days. LCs mediated HIV-1 transmission was determined via measuring infection of CCR5 Jurkat T cells by intracellular p24 staining or GFP expression in combination with T cell-marker CD3 and LC-marker CD1a following flow cytometry. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments.
