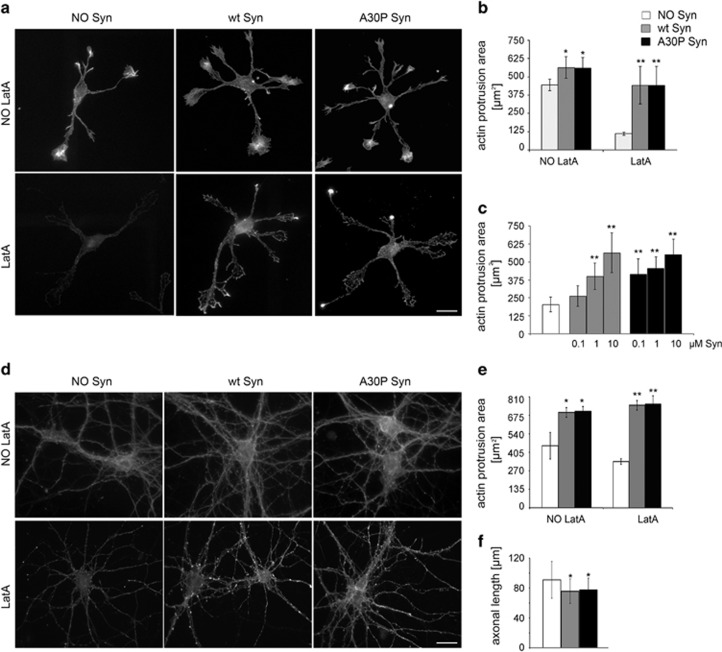
Figure 1.
Extracellular wt and A30P Syn affect actin cytoskeleton. (a) F-actin distribution, as revealed by fluorescent phalloidin staining, in 1 DIV embryonic hippocampal neurons incubated in the absence or presence of 1 μM purified wt or A30P Syn for 1 h and examined either under control conditions (NO LatA), or after a 1 h incubation with 1 μM LatA (LatA). (b) Quantitative evaluation of actin protrusion areas in neurons treated as in a. Actin protrusion areas were calculated by subtracting projection areas of β-tubulin III immunofluorescence from F-actin projection areas. (c) Dose-dependent effects of extracellular Syns on actin protrusion areas. Neurons were treated for 1 h with increasing concentrations of purified wt or A30P Syn, and then exposed to LatA for an additional hour (NO Syn: neurons not treated with Syn). Actin protrusion areas were calculated as in b. (d) F-actin distribution in 14 DIV embryonic hippocampal neurons incubated in the absence or presence of 1 μM purified wt or A30P Syn for 1 h; neurons were treated and stained as in a. (e) Quantitative evaluation of actin protrusion areas of neurons treated as in a, calculated as in b. (f) Quantitative evaluation of average axonal length measured by Sholl analysis of 3 DIV embryonic hippocampal neurons incubated with or without 1 μM purified wt or A30P Syn. In b, c and e, data are expressed as mean values ±S.D.; n=60 neurons from three independent cultures. In f, data are expressed as mean values±S.D.; n=100 neurons from three independent cultures. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test for multiple comparison, *P<0.05; **P<0.01. Bar in a and d: 20 μm