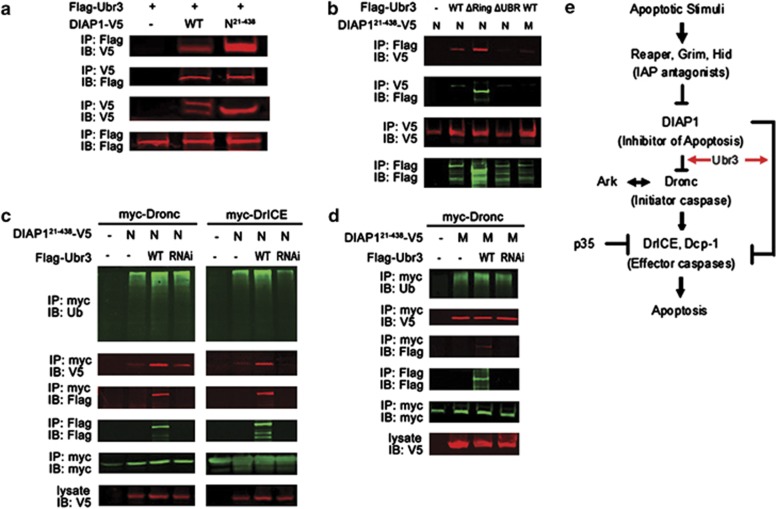
Figure 6.
DIAP1 binds to Ubr3 and promotes ubiquitination of DrICE and Dronc. (a) Co-IP assays with Ubr3 and DIAP1. S2 cells were co-transfected with V5-tagged wild-type DIAP1 or DIAP121–438 and Flag-tagged Ubr3. Co-precipitated proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. The wild-type DIAP1 exhibits two bands, the full length (top band) and the N-terminally cleaved one (low band). The interaction of Ubr3 with the cleaved DIAP1 (DIAP121–438) but not the full-length DIAP1 can be detected. (b) Co-IPs were performed as in (a) with N- and M-DIAP121–438 and the Ubr3 variants. (c) Effects of Ubr3 co-expression or knockdown on DIAP1-mediated caspase ubiquitination. S2 cells were co-transfected with myc-tagged Dronc/DrICE together with N-DIAP121-438 and constructs encoding Flag-tagged Ubr3 or Ubr3 shRNA. Half of the cells were lysed under denaturing conditions using hot lysis protocol and ubiquitinated caspases were pulled down by myc affinity gel followed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin antibody. The other half of cells were processed for co-IP assays as in (a). (d) Ubr3 fails to affect M-DIAP121-438's catalytic function in Dronc ubiquitination. Experiments were performed similar to (c). (e) Model of Ubr3's function in apoptosis. Ubr3 helps block apoptosis mainly through its interaction with DIAP1. This interaction promotes the binding of downstream caspases to DIAP1 and facilitates subsequent ubiquitination reactions