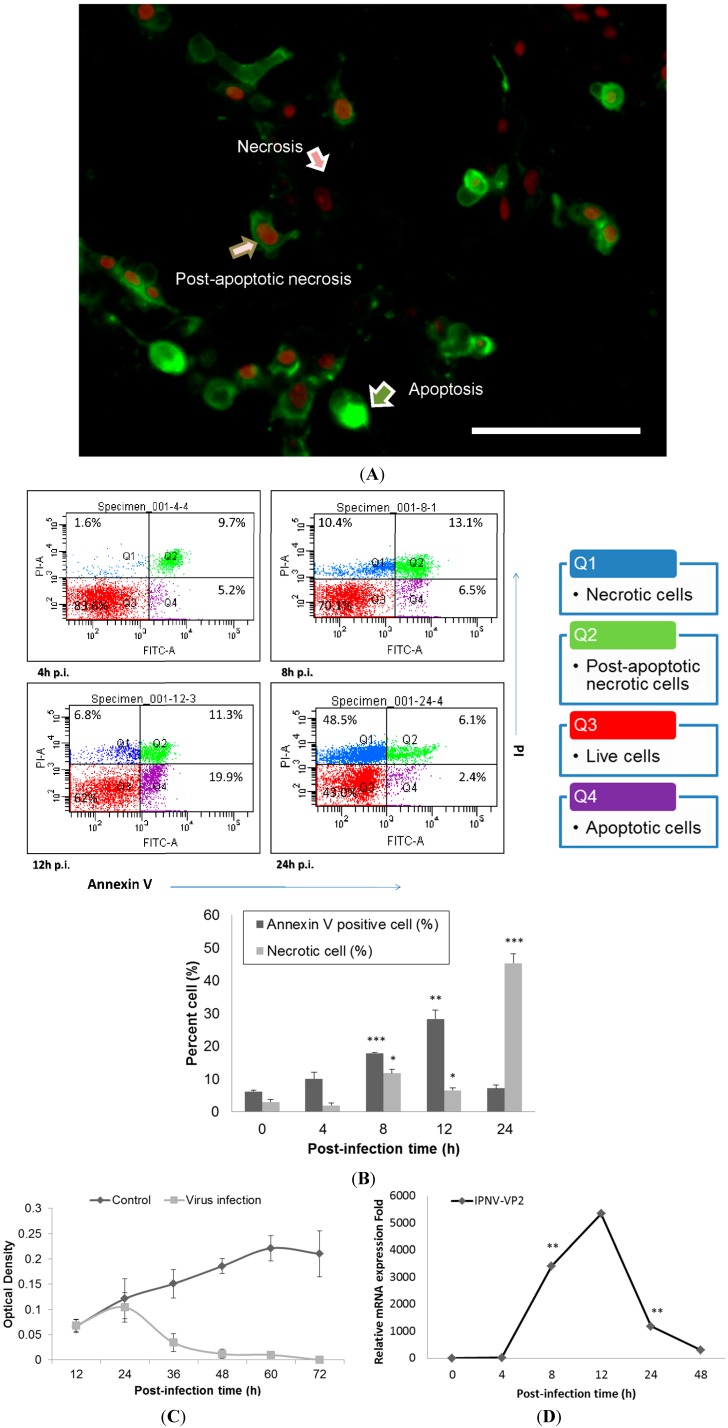
Figure 1.
Apoptosis occurs in Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV)-infected CHSE-214 cells and viral replication reaches a peak at 12 h.p.i. (MOI = 1). (A) Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining in infected CHSE-214 cells at 8 h.p.i.; three types of cells (pointed arrows) are delineated (scale bar = 100 μm). Annexin V-labeled cells indicated apoptosis, PI-labeled cells indicated necrosis, and double staining indicated post-apoptotic necrotic cells; (B) The infected cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for apoptosis, revealing a dynamic shift among the four types of cells. Double stained and PS-positive cells increased prior to 12 h.p.i., and then most cells became necrotic at 24 h.p.i. (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; and *** p < 0.0001). All reported values have been corrected for background; (C) Cell viability was determined in triplicate by a WST-1 assay, which indicated that cell viability decreased after 24 h.p.i.; and (D) Real-time qPCR to determine the mRNA levels of viral VP2, a major capsid protein of IPNV. The results indicated high levels of replication among the infected cells that peaked and corresponded to the peak in apoptosis during IPNV infection. (** p < 0.01).