Figure 1.
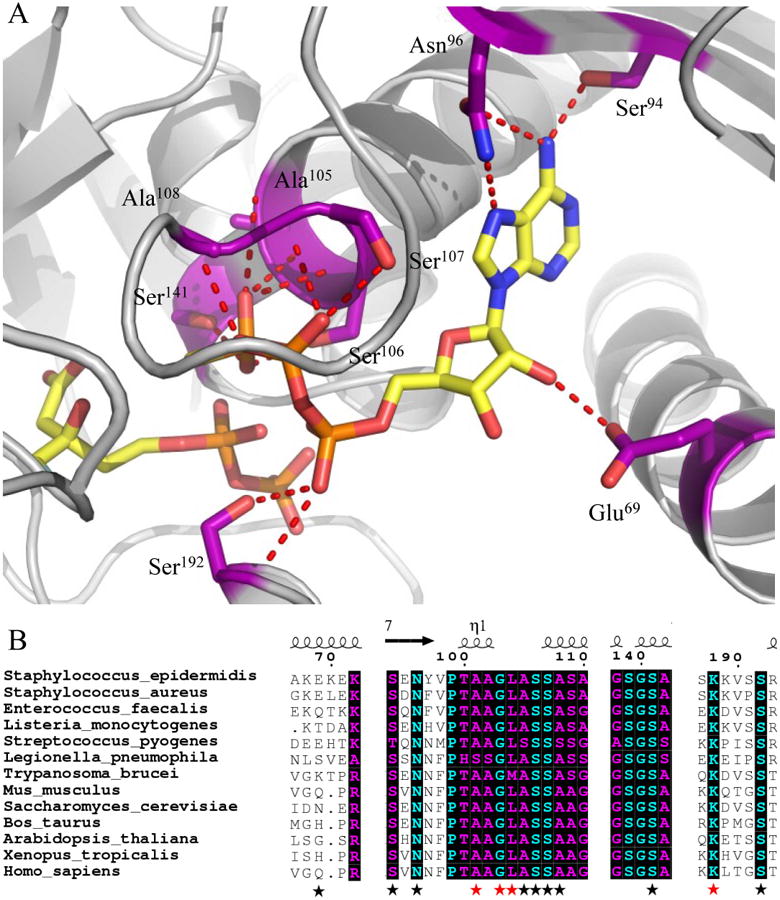
Co-crystal structure (2.19 Å) of MDD from Staphylococcus epidermidis bound to inhibitor FMVAPP and nucleotide analog ATPγS. (A) Co-crystal structure of S. epidermidis MDD in cartoon format (gray). Inhibitor FMVAPP and nucleotide analog ATPγS are represented as ball and stick (yellow). Active site side chains within interaction distance (2.5-3.4 Å) of ATPγS are depicted in ball and stick (purple) with red dashes. Hydrogen bonding distances can be found in Supplemental Table 3. (B) Limited structure-based sequence alignment of prokaryotic and eukaryotic MDD proteins colored according to residue conservation (cyan = absolute, purple = similar). Alignment was generated using ClustalW. Numbers above the sequences correspond to S. epidermidis MDD. Black stars below the sequences correspond to WT MDD amino acid side chains involved in ATPγS interaction, while red stars correspond to additional ATPγS interactions in the D283A mutant. Sequences from the following organisms were used in alignment: S. epidermidis; S.aureus; L. pneumophila; S. pyogenes; H. sapiens; S. cerevisiae; T. brucei; M. musculus; L. monocytogenes; E. faecalis; X. tropicalis; B. taurus; and A. thaliana.
