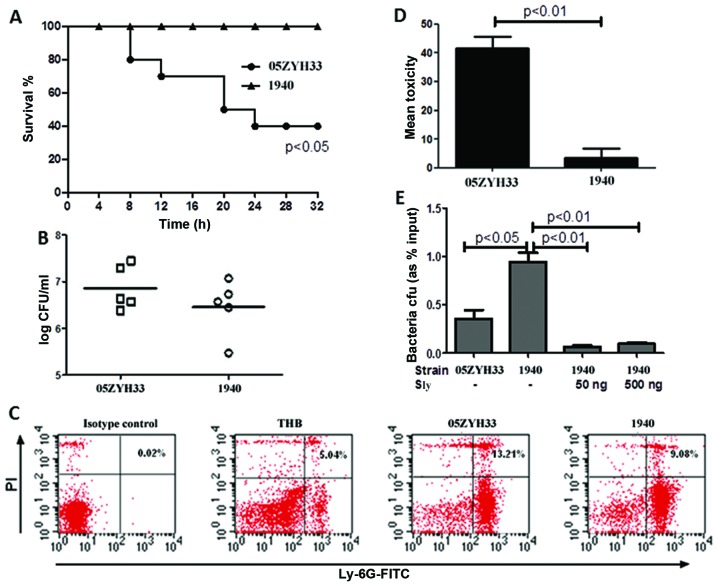
Figure 1.
Streptococcus suis epidemic strain 05ZYH33 is more virulent than the non-epidemic strain 1940. (A) CD1 female mice were intraperitoneally injected with 108 CFUs of living S. suis 05ZYH33 and 1940 in 0.1 ml sterile saline. The mortality of mice was recorded at 4-h intervals for 32 h. Cumulative results from three independent experiments, each with 10 animals per group, are shown. (B) Bacteria in the blood (n=5, per group) were counted at 5 h post-infection. (C) The necrosis of PMNs in mice infected by different bacterial strains was assayed using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-mouse anti-Ly-6G and propidium iodide (PI) staining. Data represent the values obtained in four independent experiments. THB, Todd-Hewitt broth. (D) S. suis 05ZYH33 or 1940 (108 CFUs) were incubated with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (MOI =100) for 4 h. Cytotoxicity was determined by the lactate dehydrogenase release assay. The data represent the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. (E) Pre-opsonised S. suis 05ZYH33 or 1940 (107 CFUs) were incubated with purified human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (MOI =1) in the presence or absence of recombinant sly protein for 15 min. The number of bacteria phagocytized by the PMNs was counted.