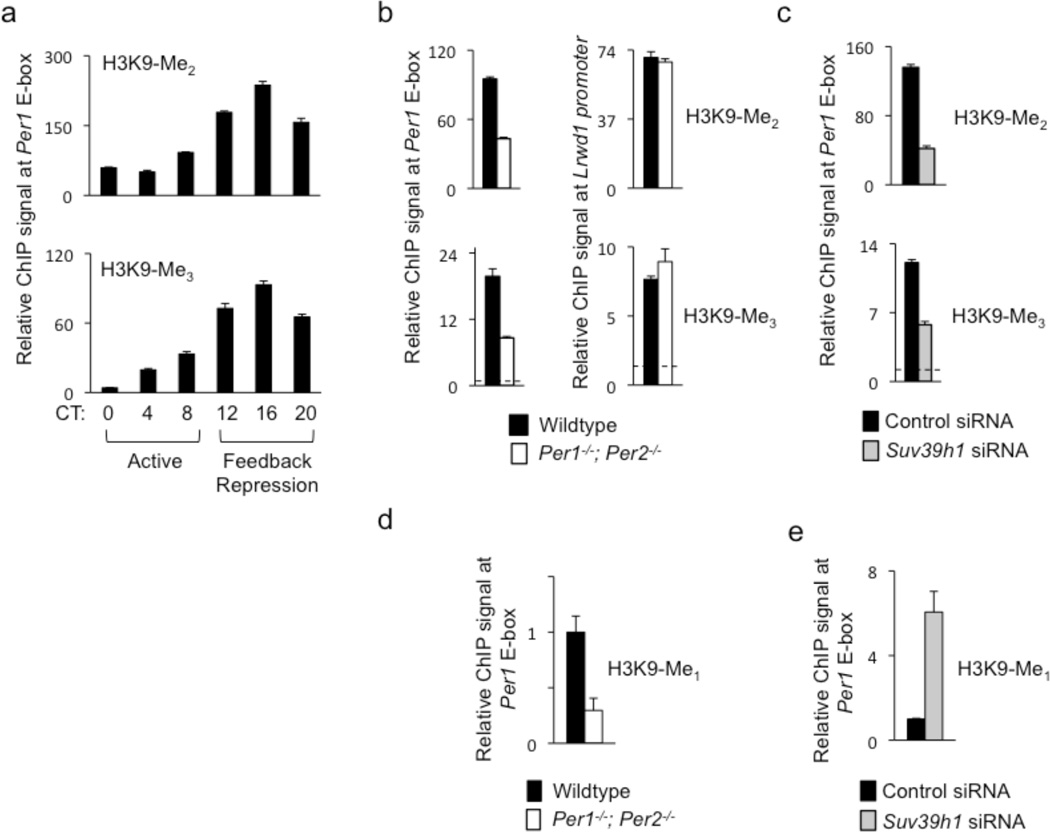
Figure 5.
PER proteins and SUV39H1 are important for di- and tri-methylation of H3K9 at the Per1 promoter. (a) Circadian cycle of di-methylated (top) and tri-methylated (bottom) H3K9 at Per1 proximal E-box site. ChIP assays are from mouse livers sampled across a circadian cycle (bottom). ChIP values are relative to the signal from parallel IgG control. (b) ChIP assays showing di-methylated (top) and tri-methylated (bottom) H3K9 at Per1 proximal E-box site in livers (CT18) of wild-type littermates (black) or Per1−/−; Per2−/− double mutant mice (white). (c) ChIP assays showing di-methylated (top) and tri-methylated (bottom) H3K9 at Per1 proximal E-box site in unsynchronized mouse fibroblasts after introduction of point-mutant control Suv39h1 siRNA (black) or after depletion of SUV39H1 by effective Suv39h1 siRNA (gray). (d) ChIP assays showing mono-methylated H3K9 at Per1 proximal E-box site in livers (CT18) of wild-type littermates (black) or Per1−/−; Per2−/−- mutants (white). (e) ChIP assays showing mono-methylated H3K9 at Per1 proximal E-box site in unsynchronized mouse fibroblasts after introduction of point-mutant control Suv39h1 siRNA (black) or after depletion of SUV39H1 by effective Suv39h1 siRNA (gray; normalized to control condition). All data are displayed as mean +/− SEM of triplicate experiments; panels (a)–(c) are representative of three independent experiments and (d) and (e) are representative of two independent experiments.