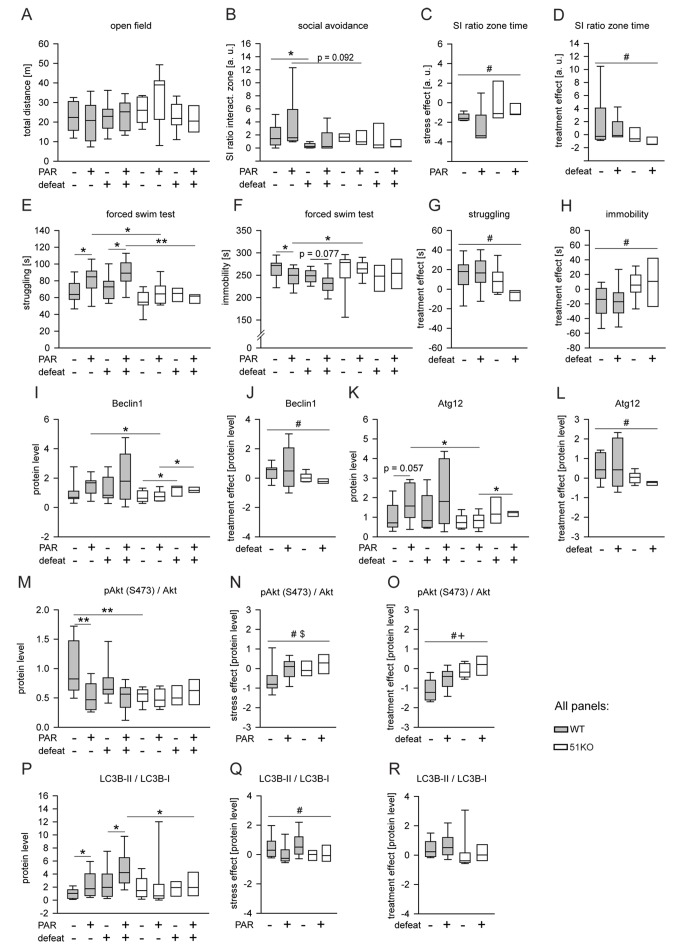
Figure 5. FKBP51 is required for the chronic effects of PAR on behavior and autophagic pathways.
Wild-type and 51KO mice were subjected to CSDS and subsequent chronic PAR treatment resulting in eight experimental groups (n = 8–12 per group) that were analyzed for behavior and autophagy marker protein levels. When the three-way ANOVA indicated an interaction effect (p<0.1), genotype-dependent stress and treatment effects were isolated by normalizing the data to either unstressed controls or vehicle treatment. (A) General locomotion in the open-field arena was independent of genotype, condition, or treatment of the mice. (B–D) Deletion of FKBP51 abolished the reaction to CSDS and to chronic PAR treatment in the social avoidance test. (E–H) Deletion of FKBP51 significantly reduced the effect of chronic PAR treatment in the FST. (I–R) Deletion of FKBP51 abolished the effects of chronic PAR treatment on the autophagy pathway markers Beclin1, Atg12, pAkt, and LC3B-II/I. Protein parameters were analyzed in hippocampal brain extracts. Asterisks indicate significant result for planned contrast test for main genotype effect (#), main treatment effect ($), or main condition effect (+): *p<0.05; **p<0.01. a.u., arbitrary units; SI zone, social interaction zone; WT, wild type.