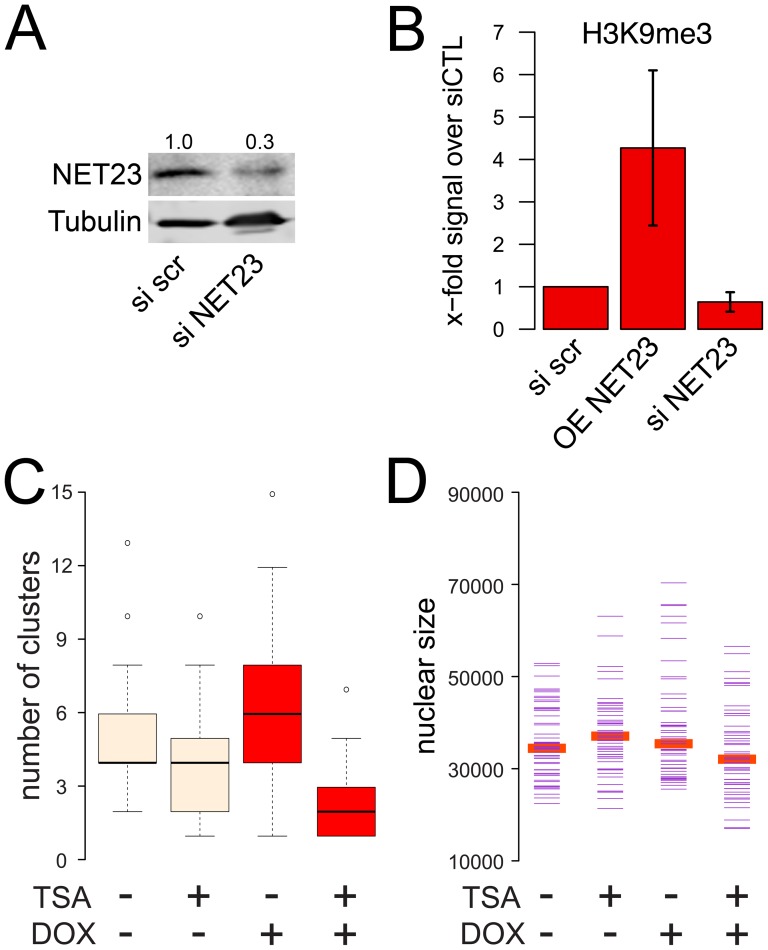
Figure 11. Modulation of NET23/STING levels changes levels of epigenetic marks and the chromatin compaction is reversible by treatment with TSA, a deacetylase inhibitor.
(A) Knockdown of NET23/STING. HT1080 cells were treated with either siRNA oligos for NET23/STING or a scramble control siRNA oligo. With this treatment NET23/STING protein levels could be reduced to 30% of initial levels at 4 d post-transfection. (B) Cell lysates were generated from a population of HT1080 cells either treated with the scramble control or NET23/STING siRNAs or a stably-transfected HT1080 line induced to express NET23/STING with doxycycline. Staining for the total levels of the H3K9me3 mark in these populations revealed that overall levels of H3K9 methylation were increased roughly 4-fold by exogenous expression of NET23/STING while overall levels appeared to be slightly reduced in the NET23/STING knockdown cells. The average from 3 experiments is shown with standard deviations. (C–D) The stably-transfected inducible NET23/STING cell line was either not treated or treated with 1 µg/ml of the histone deacetylase inhibitor TSA with or without induction of exogenous NET23/STING by doxycycline (DOX). (C) The number of high-intensity pixel clusters measured with the unbiased chromatin compaction algorithm is shown. NET23/STING induction increases the number of clusters while TSA completely reverses this effect. (D) Nuclear size was also quantified, revealing that neither doxycycline nor TSA treatment yielded any noticeable effect on nuclear size.