Figure 1.
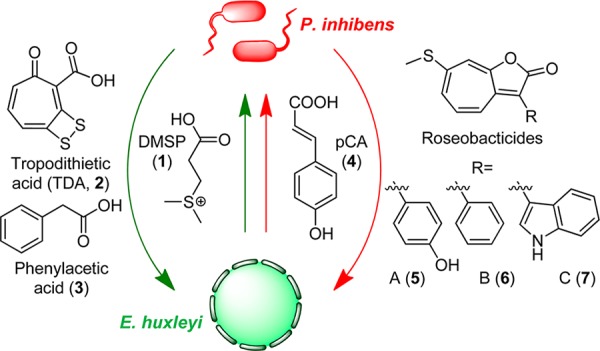
Model for metabolite exchange in the algal-bacterial symbiosis between E. huxleyi and P. inhibens. The symbiotic interaction comprises two phases, a mutualistic phase (green arrows) and a parasitic phase (red arrows). In the mutualistic phase, E. huxleyi provides the C- and S-source 1. The bacteria in return produce 2, an antibiotic that protects the host from bacterial pathogens, and 3, an algal growth promoter. In the parasitic phase, P. inhibens generates the algaecidal roseobacticides (5–7) in response to 4, a likely senescence signal produced by E. huxleyi.
