Figure 1.
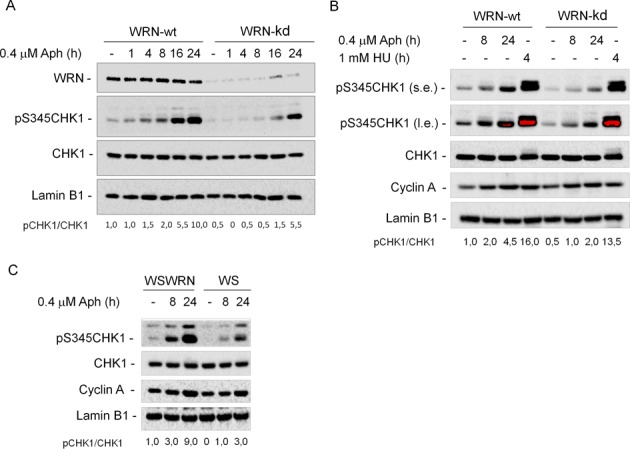
WRN is required for CHK1 activation following mild replication stress. (A) WB detection of CHK1 phosphorylation in total extracts of WRN-wt and WRN-kd cells untreated (-) or treated with Aph, as indicated. In WRN-kd cells, downregulation of the WRN protein was verified using a specific anti-WRN antibody. The presence of activated, i.e. phosphorylated, CHK1 was assessed using S345 phospho-specific antibody (pS345). Total amount of CHK1 was determined with an anti-CHK1 antibody. Equal loading was confirmed probing with an anti-Lamin B1 antibody. (B) WRN-wt and WRN-kd cells were treated with Aph or HU and processed as described in (A). (s.e., short-exposure; l.e., long-exposure). Cyclin A was used to quantify S-phase cells. (C) WRN syndrome (WS) cells and WS cells complemented with the wild-type WRN (WSWRN) were treated with 0.4 μM Aph for the indicated time. Cell lysates were analyzed by WB for the presence of phosphorylated CHK1 as described in (A). Cyclin A was used to quantify S-phase cells. The ratio of phosphorylated protein to total protein normalized to the untreated wild type is reported below each lane. All cell lines were tested at least three times and representative experiments are shown.
