Figure 4.
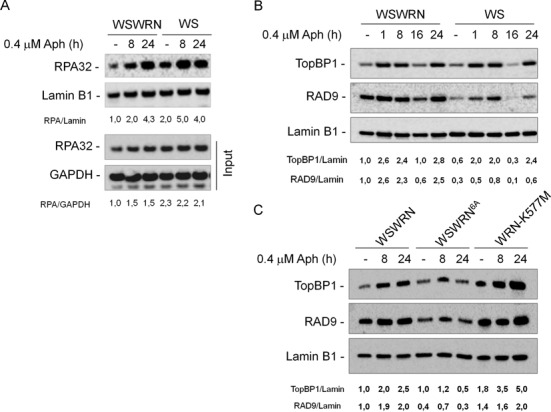
Analysis of chromatin loading of ATR-pathway sensors and mediators in cells upon mild replication stress. (A) WB analysis for chromatin loading of RPA32 in wild-type (WSWRN) and WS cells untreated or treated with Aph for various times as indicated. WB analysis of chromatin recruitment of RPA32 in WSWRN and WS cells. Total amount of RPA32 was determined with an anti-RPA32 antibody. Lamin B1 was used as loading control. WB of whole cell extracts (Input) is reported.The ratio of the RPA32/Lamin B1 signal (chromatin) or of the RPA32/gliceraldeide-3-fosfato deidrogenasi (GAPDH) signal (input) has been normalized to that of wild-type and it is reported below each lane. (B) WSWRN and WS cells were treated with Aph for various times or left untreated as indicated. Total amount of TopBP1 and RAD9 were determined with an anti-TopBP1 or anti-RAD9 antibody, respectively. Lamin B1 was used as loading control. (C) WSWRN cells and WS cells expressing an ATR-unphosphorylable form of WRN (WSWRN6A) or mutant form of WRN helicase (WRN-K577M) were treated or not with Aph for the indicated times. Total amount of TopBP1 and RAD9 and equal loading of total proteins were determined as in (B). The ratio of the TopBP1/Lamin B1 signal or of the RAD9/Lamin B1 has been normalized to that of wild-type and then reported below each lane. All experiments are representative images of at least three replicates.
