Figure 6.
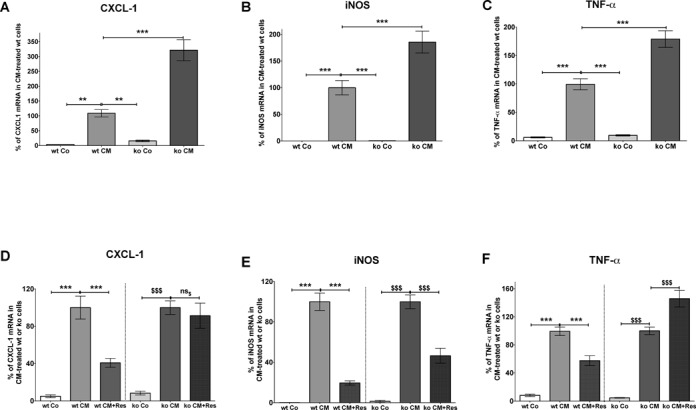
Inactivation of the KSRP gene enhances CXCL-1, iNOS and TNF-α mRNA expression and alleviates the resveratrol effect in murine peritoneal cells. Peritoneal cells were isolated from KSRP+/+ (wt) and KSRP−/− (ko) mice. Adherent cells (mostly monocytes/macrophages) were used for the experiments. (A–C) Adherent peritoneal cells were incubated with LPS (2 μg/ml) and IFN-γ (100 U/ml) to induce pro-inflammatory mRNA expression. After 2–6 h cells were lyzed and the expression of CXCL-1, iNOS, TNF-α and GAPDH (for normalization) mRNA was measured. CXCL-1, iNOS and TNF-α mRNA expression was normalized to GAPDH mRNA expression. The CM-induced mRNA expression in KSRP+/+ (wt) cells was set to 100%. Shown are the mean ± SEM of n = 8–10 analyses (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01 versus CM-treated cells isolated from KSRP+/+ mice; one-way ANOVA). (D–F) Adherent peritoneal cells were pre-incubated with 30 μM resveratrol (Res) for 1 h and then treated with LPS (2 μg/ml) and IFN-γ (100 U/ml) for additional 2–6 h. RNA was isolated and the expression of CXCL-1, iNOS, TNF-α and GAPDH (for normalization) mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. CXCL-1, iNOS and TNF-α mRNA expression was normalized to GAPDH mRNA expression. The mRNA expression in CM-treated KSRP+/+ (wt) or KSRP−/− cells (ko) was set to 100%. Shown are the mean ± SEM of n = 8–10 analyses (***P < 0.001 versus CM-treated cells isolated from KSRP+/+ mice; $$$P < 0.001; ns$, not significant versus CM-treated cells isolated from KSRP−/− mice; one-way ANOVA).
