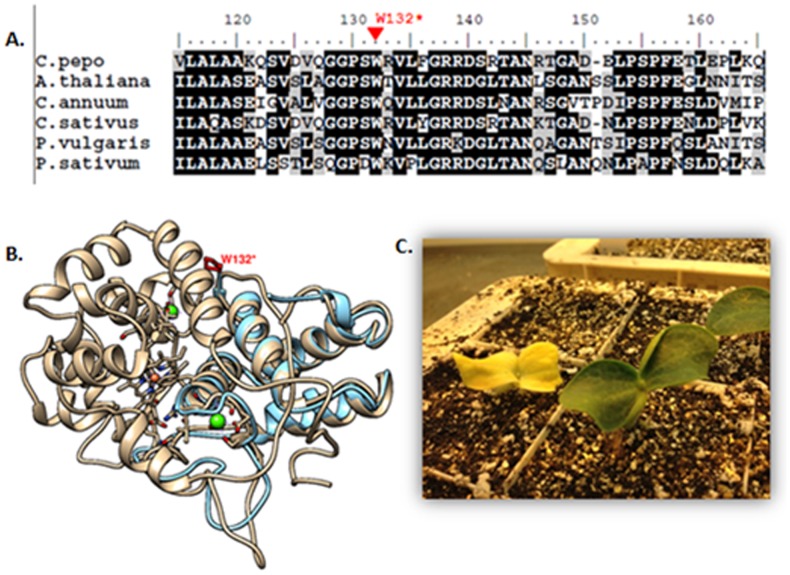
Figure 3. Sequence and structural analysis of APRX.
(A) Amino acid alignment of Cucurbita pepo APRX and homologous proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana (AAM66044.1), Capsicum annun (AFU51540.1), Cucumis sativus (AAA33128.1), Phaseolus vulgaris (AAD37427.1) and Pytum sativus (BAD97438.1). Numbers above the alignment indicate the amino acid positions along the APRX protein. The EMS-induced stop mutation in W132 is shown above the alignment in red. (B) Superposition of the predicted 3D structure model of APRX WT protein indicated in grey and the mutant protein indicated in blue. The proximal heme pocket is represented in red and the two calcium ions in green. The position of the induced stop codon mutation indentified in Cp-161 family (W132*) is indicated in red. The APRX model was determined using the Geno3D server (http://geno3d-pbil.ibcp.fr). (C) Wild type and albino phenotypes observed in line Cp-161.