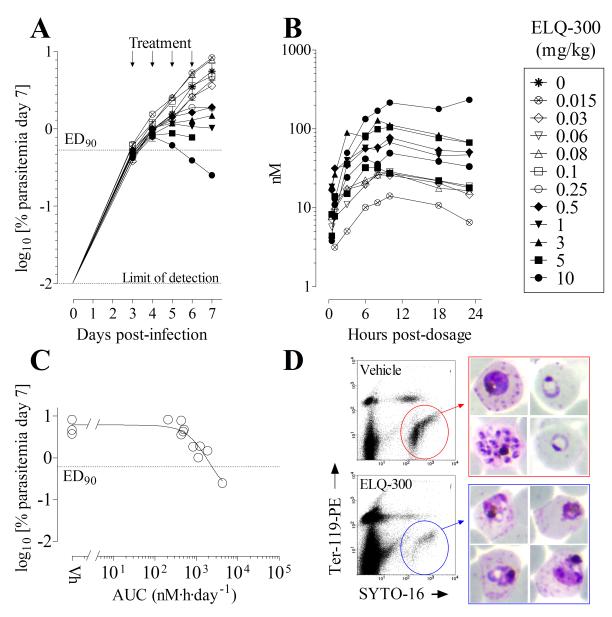
Figure 6.
Efficacy of ELQ-300 against the human malaria parasite in the immune-deficient (SCID) humanized mouse model of P. falciparum. A group of 3 mice treated with vehicle and another group of 11 mice treated with different doses of ELQ-300 were analyzed to estimate ED90 and AUCED90 as parameters of efficacy. (A) Parasitemia in individual mice treated with different doses of ELQ-300 during the efficacy assay. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. (B) Concentrations of ELQ-300 in the blood of each individual mouse in the efficacy study measured for 24 h after the initial oral dose administration. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. (C) Graphic estimation of AUCED90 for ELQ-300. Data are the area under the curve for ELQ-300 in blood during the first 24 h after first oral dose administration (AUC0→23h) vs log10 [parasitemia at day 7] for each individual mouse in the efficacy study. (D) Microscopic and flow cytometry analysis of P. falciparum present in peripheral blood of mice treated with vehicle or ELQ-300. Samples were taken 48 h after the start of treatment (i.e., 1 cycle of exposure to drug). Flow cytometry dot plots from samples of peripheral blood show P. falciparum infected human erythrocytes inside of the polygonal regions. Images in the right hand panels show Giemsa-stained bloodstream parasites present at the 48 h time point. Blood films from control untreated animals show normal staining and appearance while the parasites in ELQ-300 treated animals stain poorly and exhibit altered morphology.