Figure 1. A high-affinity T cell epitope incorporated into Q11 nanofibers induces antigen-specific T cell responses.
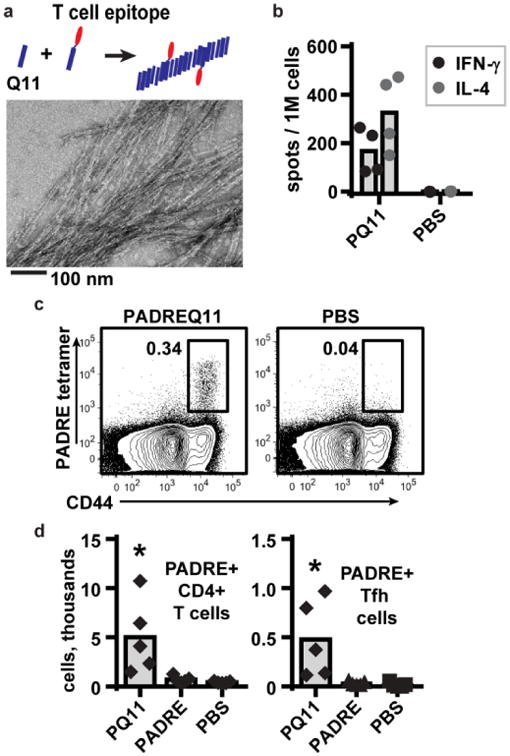
(a) PADRE, a high-affinity CD4+ T cell epitope[21], was synthesized in tandem with the Q11 assembly domain and mixed into unconjugated Q11 to form integrated assemblies observable by TEM (0.05 mM PADRE-Q11, 1.95 mM Q11). (b) Mice were immunized with PADREQ11 (0.05 mM PADREQ11 + 1.95 mM Q11) and boosted on day 14; on day 21, cells from the lymph nodes were stimulated with PADRE peptide, and the IL-4 and IFN-[3] -secreting cells were quantified by ELISPOT. (c) A PADREI-Ab tetramer was validated to detect endogenous PADRE-specific T cells (CD4+ CD44+ PADRE+) by flow cytometry. CD44 is a marker for T cells that have encountered cognate antigen. Data from one PADREQ11-immunized and one PBS-immunized mouse are shown; representative of 3 mice per group, repeated twice. (d) Immunization with PADREQ11 but not free PADRE peptide (0.05 mM PADRE in saline) generated PADRE-specific CD4+ T cells as defined above, as well as PADRE-specific Tfh cells (CD4+ PADRE+ CXCR5+ PD-1+) by 7 days after primary immunization. In b and d, each dot indicates 1 mouse, and cell numbers are quantified from the six draining lymph nodes that were collected from each mouse. Analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. Bars show average values.
