Figure 2. Co-assembled B and T epitopes raise a high-titer antibodies and a modular T cell response.
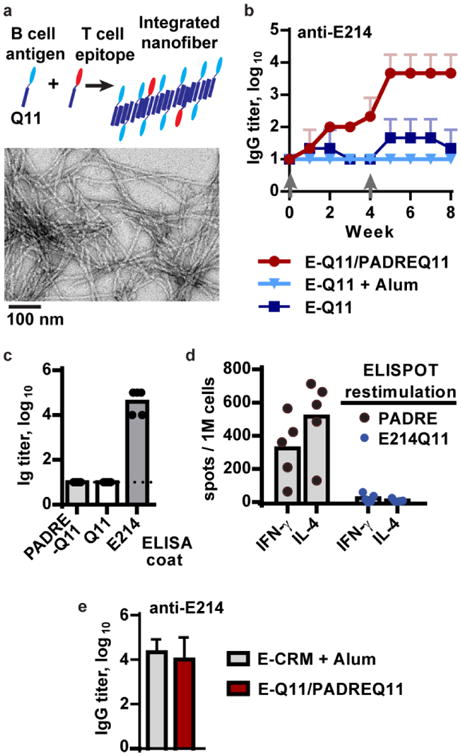
(a) In the co-assembly strategy, B cell and T cell antigens are synthesized separately in tandem with the Q11 assembly domain, then mixed in the specified ratio with unconjugated Q11 to form integrated assemblies that are visible by TEM (shown with 1 mM E214Q11, 0.05 mM PADREQ11, 0.95 mM Q11). (b) Anti-E214 responses to Q11-based vaccines required assembly with a T cell epitope, PADRE. Mice were immunized at week 0 and boosted with a half-dose of peptide at week 4 (grey arrows). E214Q11 (2 mM) failed to raise a response even when adjuvanted with Alum, whereas the co-assembled E214Q11 (1 mM)/PADREQ11 (0.05 mM) vaccine raised a strong response. n = 3 mice per group, representative of at least 2 independent experiments. (c) The antibodies were specific to only the E214 epitope, not PADREQ11 or Q11, in ELISA (serum after two boosts). (d) The T cell IL-4 and IFN-gamma responses were specific to only PADRE, not E214Q11, in ELISPOT assays (lymph nodes collected after two boosts). In (c) and (d), each dot indicates 1 mouse, with 5 mice in each group. (e) Mice immunized with alum-adjuvanted E214-CRM protein or with unadjuvanted E214Q11/PADREQ11 assemblies raised equivalent E214-specific responses. Serum was analyzed at week 9, one week after a second boost. n = 3 mice per group. All error bars show standard deviation.
