Figure 1.
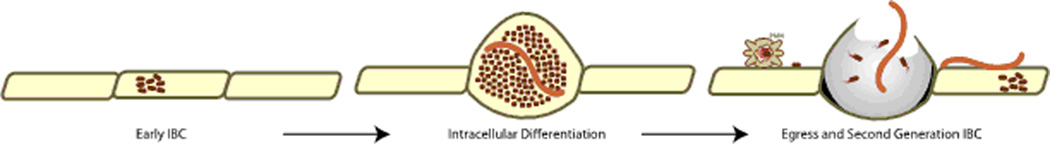
UPEC intracellular differentiation pathway. UPEC (maroon rods) invade into the cytoplasm of the bladder epithelial cell to initiate the intracellular developmental and differentiation pathway (early IBC). The epithelial cell becomes engorged with UPEC in the coccoid (dark maroon) and filamentous (light maroon) morphologies to form the pod (intracellular differentiation). The pod ultimately lyses, releasing rod and filamentous morphotypes that invade into neighboring naïve cells for persistence (egress and second generation IBC).
