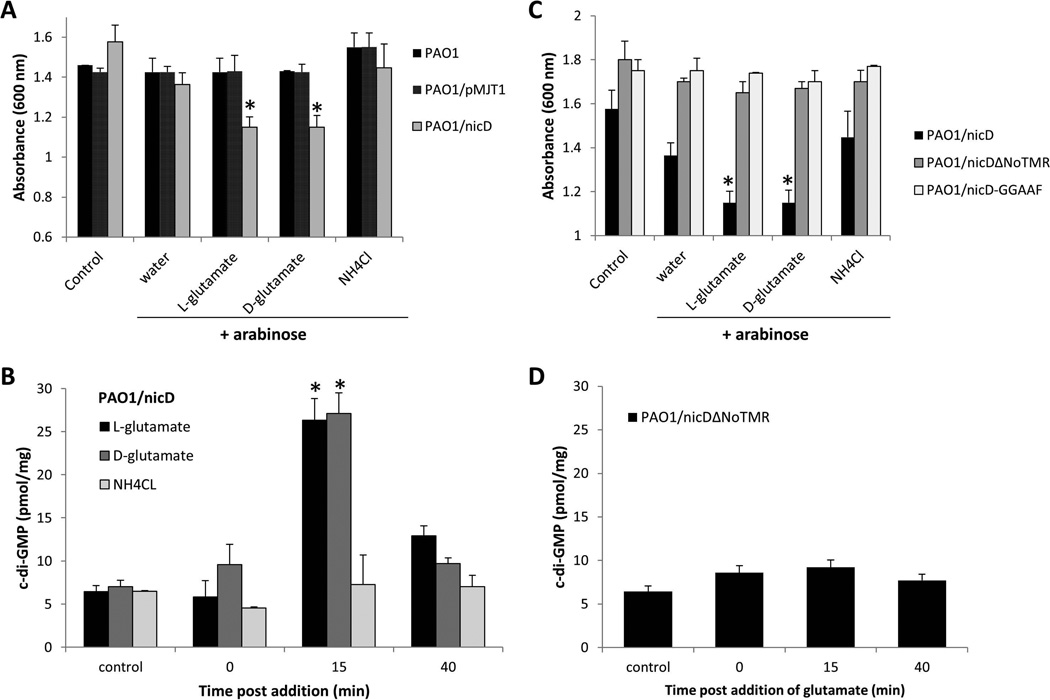
Figure 5. NicD DGC activity is induced upon exposure to glutamate, resulting in increased cellular c-di-GMP levels.
(A) Absorbance of culture medium of exponential phase P. aeruginosa PAO1/pMJT-nicD, prior to addition of arabinose (control) and following addition of arabinose (3 hr) and subsequent addition of water, D- and L-glutamate and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). PAO1 and PAO1/pMJT1 were used as vector control. Experiments were carried out at least in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviation. *, significantly different from “water” control to which only arabinose (3 hr) plus water was added. (B) Cellular c-di-GMP levels in PAO1/nicD following addition of arabinose (3 hr, control), and 0, 15 and 40 min post-addition of D- and L-glutamate and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). Experiments were carried out at least in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviation. *, significantly different from 0 min time point. (C) Absorbance of culture medium of exponential phase P. aeruginosa PAO1 overexpressing nicD, nicDΔNoTMR, or nicD-GGAAF, prior to addition of arabinose (control) and following addition of arabinose (3 hr) and subsequent addition of water, D- and L-glutamate and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). Experiments were carried out at least in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (D) Cellular c-di-GMP levels in PAO1/nicDΔNoTMR mutant following addition of arabinose (3 hr), and 0, 15 and 40 min post-addition of glutamate. Experiments were carried out at least in triplicate. Error bars indicate standard deviation.