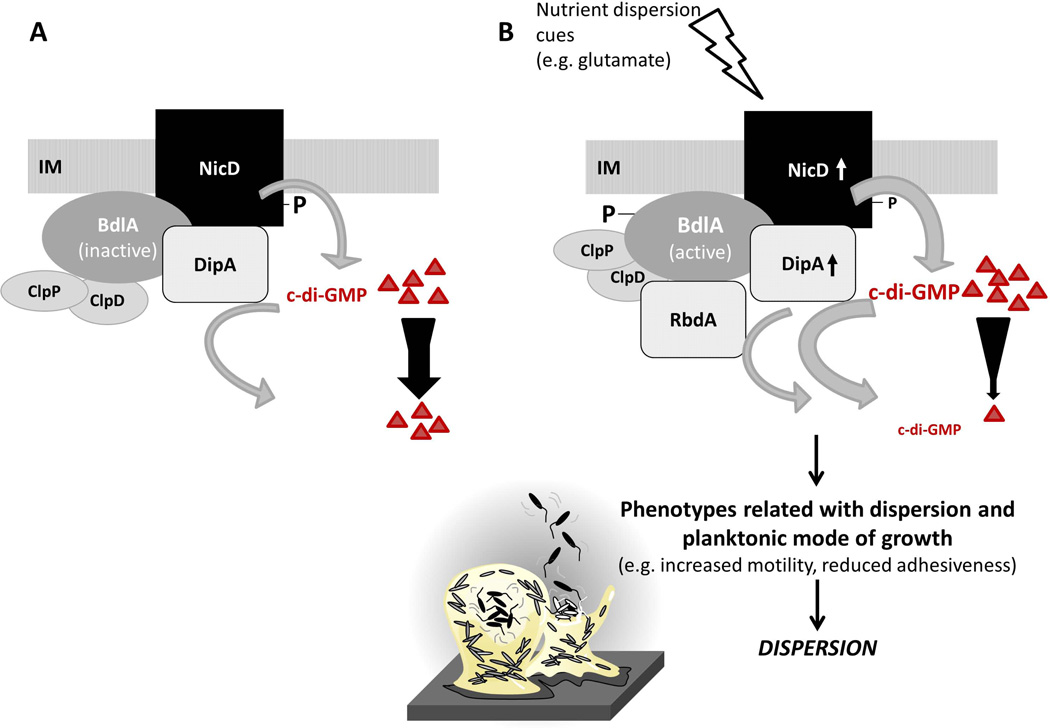
Figure 9. Model of signal transduction upon sensing the dispersion-inducing cue glutamate.
(A) The diguanylate cyclase NicD is membrane-bound and phosphorylated. NicD forms a multiprotein complex with the phosphodiesterase DipA and the sensory protein BdlA. BdlA is intact but inactive under planktonic growth conditions (Petrova & Sauer, 2012a). BdlA interacts with the chaperone ClpD and the protease ClpP (Petrova & Sauer, 2012a). (B) Upon perceiving a dispersion-inducing nutrient cue, e.g. glutamate, NicD is dephosphorylated and its diguanylate cyclase activity increases, resulting in elevated levels of c-di-GMP. BdlA is phosphorylated. Both phosphorylation and elevated levels of c-di-GMP contribute to BdlA being cleaved in a non-processive manner, a process requiring the chaperone ClpD, the protease ClpP, and BdlA phosphorylation at Y238 (Petrova & Sauer, 2012a). Cleaved BdlA is active with respect to enabling P. aeruginosa biofilms to respond to dispersion inducing conditions (Petrova & Sauer, 2012a). Active BdlA in turn enhances the activity of the phosphodiesterase DipA, resulting in decreased c-di-GMP levels. It has been well demonstrated that increased DipA activity results in decreased biofilm c-di-GMP levels (Basu Roy et al., 2012). Moreover, active BdlA was recently demonstrated to interact with the phosphodiesterase RbdA in vivo (Petrova & Sauer, 2012b). The recruitment of RbdA to the multiprotein complex likely further contributes to the observed reduction of c-di-GMP in dispersed cells compared to biofilm cells (Basu Roy et al., 2012, An et al., 2010, Barraud et al., 2009). Dispersion has been described to require or coincide with the breakdown of extracellular polymeric matrix surrounding the biofilms, induction of flagellar gene expression, increased motility, and reduced adhesiveness (Morgan et al., 2006, Sauer et al., 2002, Sauer et al., 2004, Basu Roy et al., 2012). IM, inner membrane; triangles and number of triangles represent c-di-GMP and cellular c-di-GMP levels. P, phosphorylation. Size of P correlates with level of phosphorylation. Arrows associated with NicD and DipA indicate increased enzyme activity. Width of grey arrows indicates level of activity.