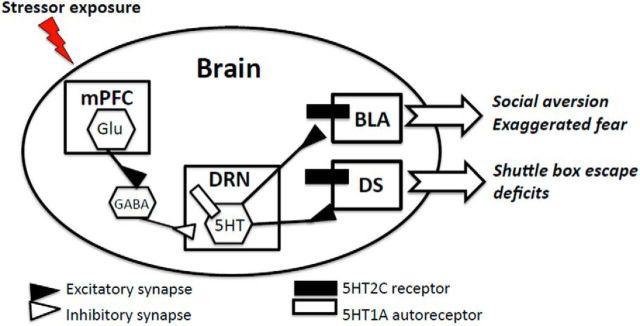
Figure 3.
Working model of the 5HT neural circuit responsible for the emotional (social aversive and exaggerated fear) and cognitive (shuttle box escape deficit) impact of uncontrollable stress in rats. Regular, moderate physical activity (6 weeks wheel running) produces adaptations in the circuit that include upregulation of 5HT1A inhibitory autoreceptors on DRN cell bodies and a downregulation in 5HT2C receptors in DRN projection sites, amygdala (AMG) and dorsal striatum (DS). Together, these changes constrain the 5HT response to uncontrollable stress and prevent neural sensitization and the expression of learned helplessness behaviors.