Figure 4.
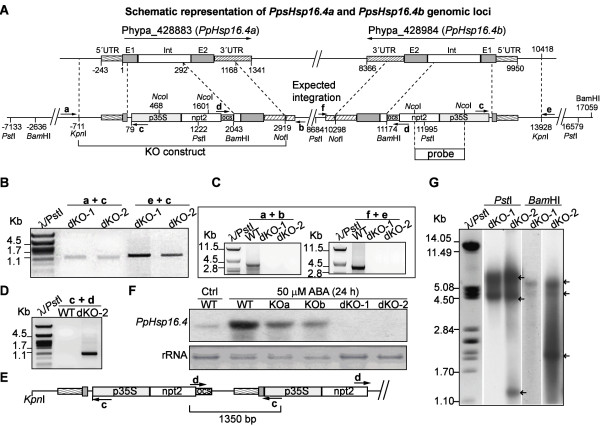
Targeted insertion at PpHsp16.4a and PpHsp16.4b loci. (A) Structure of PpHsp16.4 genomic loci and expected outcome of construct integration. Exons (E1 and E2) and intron (Int) are boxed. The position of the primers used for PCR analysis of wild type (WT) and mutants is indicated with arrows (B) PCR analysis of double knockouts (dKO-1 and dKO-2). Amplification of the 5’ DNA junction sequence for identification of targeting events in PpHsp16.4a was done using primer a, located upstream of the construct sequence, in conjunction with primer c, specific for the targeting construct. The 5’region of insertion events in PpHsp16.4b was characterized using primer e, specific for the 5’ genomic sequence flanking the construct, together with primer c. The size in kilo base pairs (kb) of the molecular weight marker (λ/PstI) is shown to the left. (C) PCR amplification of the genomic sequence of PpHsp16.4 loci. Amplification of PpHsp16.4a was done using primers a and b, specific for the flanking 5’and 3’sequences respectively. Amplification of PpHsp16.4b, was done using the external primers f and e. (D) Detection of construct concatemers using primers c and d, specific for the targeting construct. (E) Schematic representation of a partial head-to-tail structure of concatenated DNA revealed by sequencing of the PCR product obtained in (D). (F) Northern blot analysis of WT, single knockout lines (KOa, KOb), and double knockout lines. Total RNA isolated from plants treated with 50 μM ABA for 24 h or control (Ctrl) was hybridized to the radiolabeled full-length cDNA sequence of PpHsp16.4. Ethidium bromide staining of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) was used to ensure equal loading of RNA samples. (G) Southern blot analysis of WT, dKO-1 and dKO-2 genotypes. Genomic DNA was digested with PstI and BamHI, and hybridized with a radiolabeled DNA probe shown in (A). Arrows indicate hybridization bands.
