Figure 3.
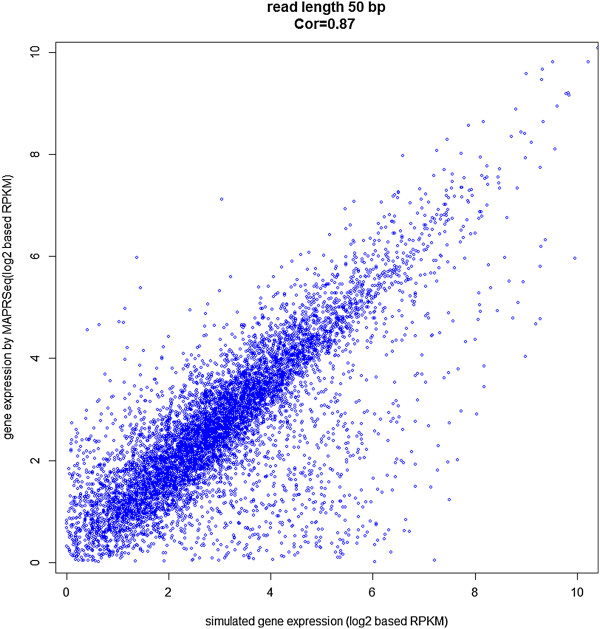
Correlation of gene counts reported by MAP-RSeq in comparison to counts simulated by BEERS. MAP-RSeq uses the HTSeq software to classify reads to genomic features. The intersection nonempty mode of HTSeq was applied and the query-name sorted alignment (BAM) file along with the reference GTF file obtained from BEERS were provided as input files to HTSeq for accurate assignment of paired-end reads to genomic features. Comparison of the gene counts (RPKM) obtained from MAP-RSeq with counts for respective genes simulated by BEERS yielded a Pearson correlation of 0.87. The genomic regions where gene expression reported by HTSeq did not completely correlate with simulated expression are due to ambiguous reads or due the fact that either mate of the paired-end read mapped to a different genomic feature, thus categorizing the read as ambiguous by HTSeq.
