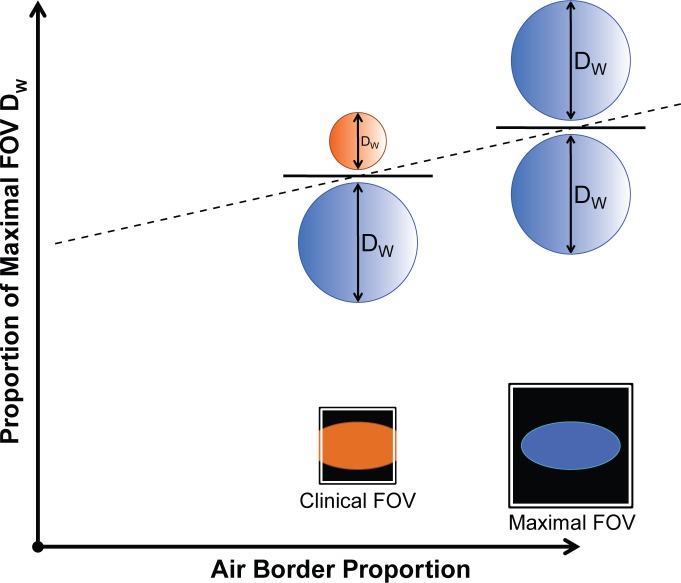
Figure 3:
Effect of clinical image truncation. The air border proportion is the proportion of image border pixels that contain attenuation values less than −600 HU. If there is no image truncation (schematic patient contour as blue ellipse with maximal FOV), the air border proportion is one (all border pixels contain air), resulting in extraction of the full patient DW (blue circles). In routine clinical image reconstruction, the peripheral soft tissues are often truncated (orange ellipse with clinical FOV) to focus on the anatomy of interest, resulting in a reduced air border proportion, and a reduced DW (orange circle).