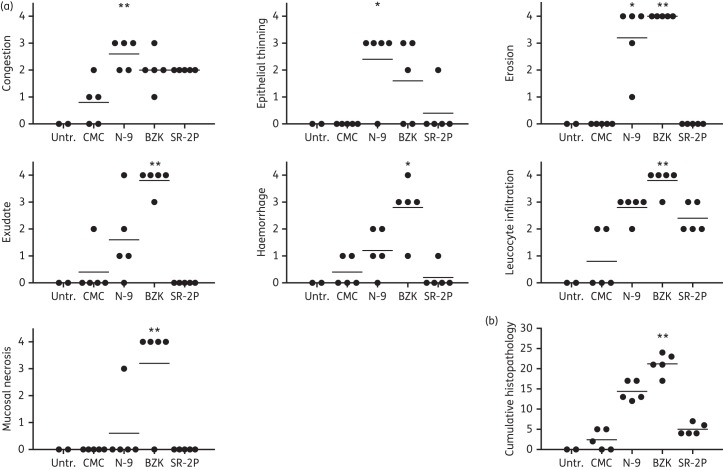
Figure 5.
Semi-quantitative histopathology analysis in a rabbit vaginal irritation safety model. NZW rabbits were dosed intravaginally once daily with 2% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC; vehicle), 8% nonoxynol-9 (N-9) in 2% CMC, 2% benzalkonium chloride (BZK) or SR-2P (n = 5). Untreated animals (Untr.) were used as controls (n = 2). After 10 treatment days, vaginal tissues were collected and sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin. Slides were analysed by a board-certified pathologist for individual histopathology parameters (congestion, epithelial thinning, erosion, exudate, haemorrhage, leucocyte infiltration and mucosal necrosis) and scored semi-quantitatively on a scale of 0–4: 0 = not observed; 1 = minimal; 2 = mild; 3 = moderate; and 4 = marked (filled circles). Cumulative histopathology scores were calculated as the sum of the individual parameters. Whereas N-9 and BZK treatment increased individual histopathology parameters significantly compared with CMC vehicle control treatment, no significant histopathology was observed after SR-2P treatment. Data were analysed by Kruskal–Wallis test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.