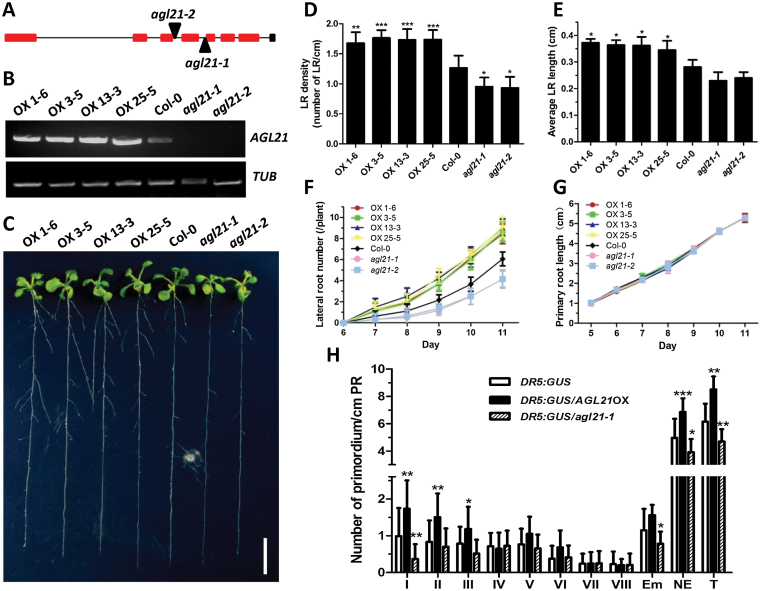
Figure 1.
AGL21 Is Involved in LR Development.
The seeds were germinated for 5 d on MS medium, and the seedlings were then transferred to MS medium for vertical growth.
(A) AGL21 gene structure with the sites of T-DNA insertion. Squares correspond to exons while lines represent introns.
(B) AGL21 transcript levels in the transgenic lines and mutants by RT–PCR analysis. TUBULIN (TUB) was used as the internal control.
(C) Root systems of 12-day-old 35S::AGL21, agl21 mutants and wild-type (WT) (Col-0) seedlings (bar = 1cm).
(D) Density of visible LRs of 12-day-old plants. Density of visible LRs is defined as visible LR number per cm PR. Values are mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments each containing 15–20 plants per genotype. Asterisks denote Student’s t-test significance compared with WT plants: * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
(E) Average LR length of 12-day-old plants. Average LR length is defined as the ratio of total LR length over LR number. Values are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments each containing 15–20 plants per genotype. Asterisks denote Student’s t-test significance compared with WT plants: * P < 0.05.
(F, G) LR and PR growth curves of WT, agl21 mutants, and 35S::AGL21 plants.
(H) Numbers of LRP of 8-day-old seedlings at given stages. Stages of primordia were based on the classification by Malamy and Benfey (1997). Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments each containing 15 plants per genotype and asterisks denote Student’s t-test significance compared with WT plants: * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. NE, non-emerged LR; E, emerged LR; T, NE + E