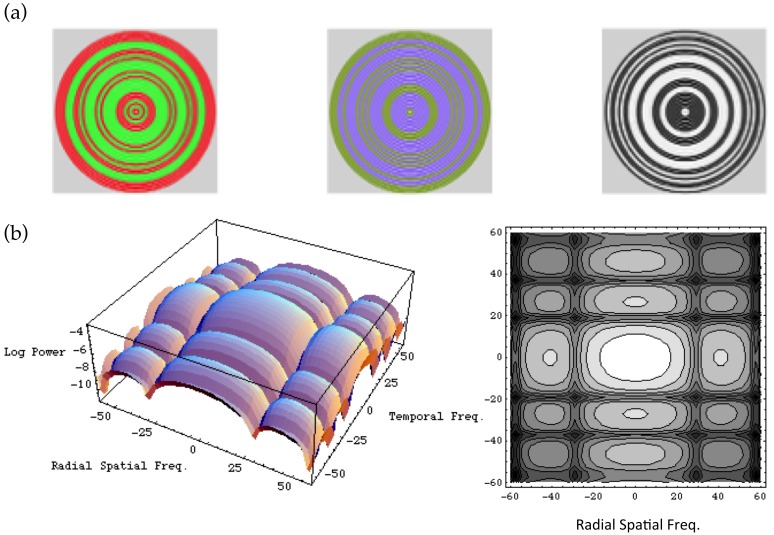
Figure 2.
Masking noise. Noise rings were binary, randomly switching between two complimentary chromaticities with probability 1/2 at 18.75 Hz. The three panels in (a) depict three examples of the noise, for L–M, S, and achromatic chromaticities. The panels in (b) show the power spectrum of the masking noise, in terms of temporal and (radial) spatial frequency, as a surface plot and a contour plot. See Appendix A.