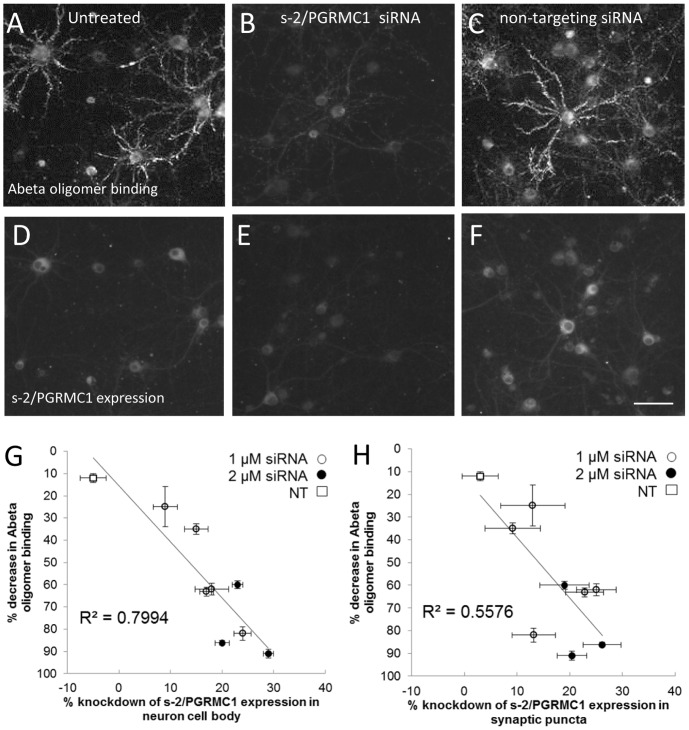
Figure 4. PGRMC1 mediates the binding of Abeta oligomers to neurons in vitro.
Co-immunolabeling for Abeta oligomer binding (A–C) and sigma-2/PGRMC1 expression (D–F) in the same field of view in hippocampal and cortical cultures (21DIV). Untreated neurons (A, D) exhibit Abeta oligomer binding to synaptic sites on neurites and low levels of sigma-2/PGRMC1 expression. In the presence of siRNA to sigma-2/PGRMC1, both Abeta oligomer binding and sigma-2/PGRMC1 expression are significantly reduced (B, E). Non-targeting siRNA (C, F) has no effect. G. H. Graphs of immunocytochemically detectable PGRMC1 protein expression associated with neuron cell bodies (G) and synaptic puncta (H), and Abeta oligomer binding to synapses for each of nine separate experiments (expressed as a percentage of untreated control culture values mean ± S.E.M.). siRNA-mediated reduction in PGRMC1 protein expression of up to 28% results in a corresponding decrease in Abeta oligomer binding by up to 91% (linear regression for PGRMC1 expression in neuronal cell bodies, r2 = 0.799, p = 0.0011; for PGRMC1 expression in synaptic puncta, r2 = 0.554, p = 0.02).