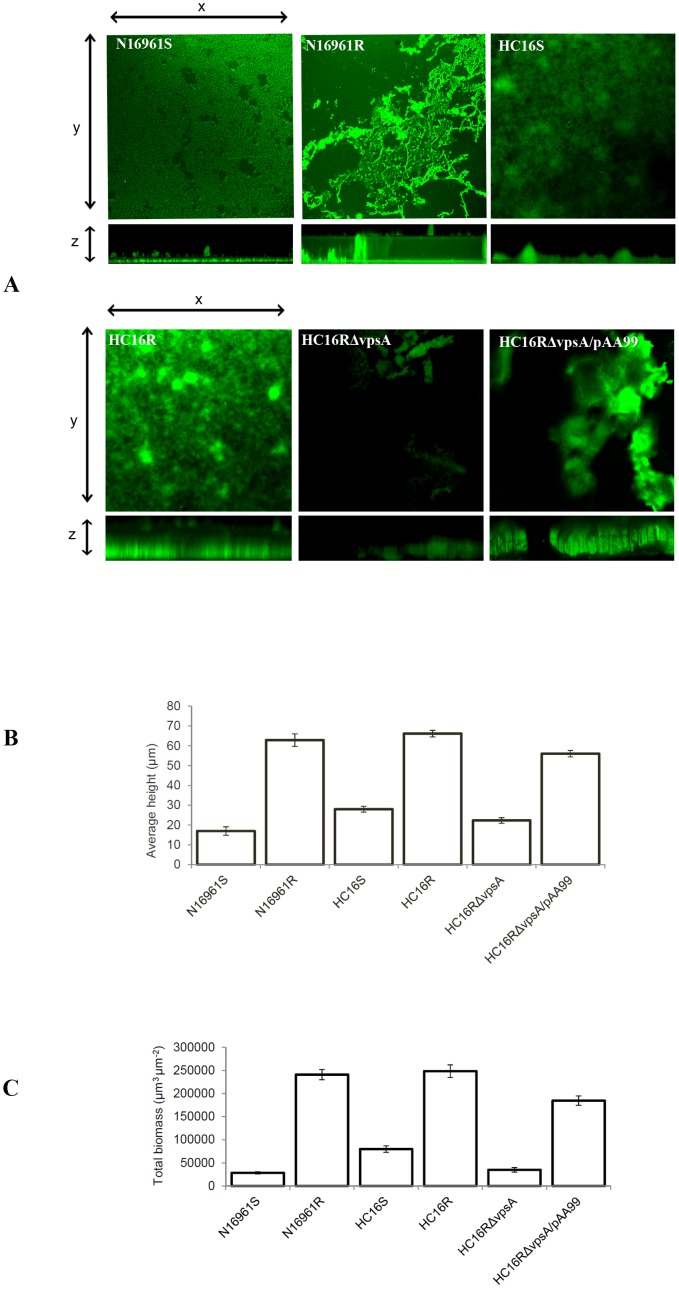
Figure 3. Topography and architecture of V. cholerae biofilms.
Each strain was grown in a 4-well cell culture plate containing 500 µl L-broth. A glass cover slip was dipped into each culture well and incubated overnight statically at room temperature. The glass cover slips were stained with SYTO 9 and the images were obtained using a laser scanning confocal microscopy with an excitation and emission wavelengths of 484- and 500 nm, respectively, as described previously [18]. (A) Images of x-y sections (top portions of panels) and x-z projections of the same biofilms (bottom portions of panels) were analyzed with DAIME software; magnification, ×200. (B) Average biofilm heights (µm) for each strain measured across five random x-z sections. (C) Total biomass of biofilm (µm3µm−2) for each strain calculated by x-y and x-z projections.