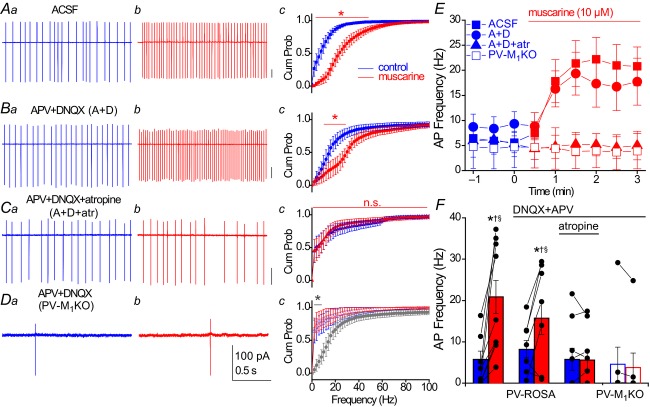
Figure 6. Muscarinic enhancement in AP frequency of hippocampal PV interneurons occurs through direct activation of M1 mAChRs.
A–C, representative recordings obtained under the following conditions: (A) ACSF conditions, (B) in the presence of ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists 50 μm APV and 20 μm DNQX or (C) in the presence of 50 μm APV, 20 μm DNQX and 5 μm atropine. A–C, from PV-Rosa mice. D, similar recordings as in (B) from a YFP+ neuron in a PV-M1KO mouse (floxed YFP AAV used to visualize PV cells). For each condition in (A–D), representative traces from 2 s long loose patch recordings from PV cells are shown in control conditions (a, blue) and after 3 min bath application of 10 μm muscarine (b, red). (c) Cumulative probability (Cum Prob) distributions of instantaneous AP firing frequencies (2 Hz bin width). A significant difference between (blue) control and (red) muscarine in Ac (ACSF: P < 0.05 from 2–50 Hz, n = 10), Bc (DNQX + APV: P < 0.05 from 10 to 32 Hz, n = 7), but not Cc (DNQX + APV + atropine: P > 0.05, n = 9) or Dc (DNQX + APV in PV-M1KO: P > 0.05, n = 7; Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank test). Dc, grey asterisk denotes a significant difference (P < 0.05 from 2 to 10 Hz) in control conditions between PV-Rosa (grey; same as Bc, blue) and PV-M1KO mice (open symbols, blue; Mann–Whitney test, n = 7.7). E, time course of change in AP frequency in conditions (A–D); muscarine was bath applied at t = 0. F, summary of the average AP frequency across conditions (A–D), comparing the average AP frequency in a 1 min region before muscarine application (blue) and a 1 min region 2–3 min after bath application of muscarine. Asterisks denote P < 0.05 for (blue) control vs. (red) muscarine conditions (Wilcoxon signed rank test, W9 = 55, P = 0.002 for ACSF conditions, n = 10; paired t test, t6 = 2.753, P = 0.033 for DNQX + APV conditions, n = 7). In muscarine conditions, AP frequency was also significantly reduced in conditions C (DNQX + APV + atropine, †) and D (DNQX + APV in PV-M1KO, §) compared to conditions A (ACSF) and B (DNQX + APV; Mann–Whitney test, P < 0.05). AP, action potential; Cum Prob, cumulative probability; M1KO, M1 mAChR knockout; mAChR, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; PV, parvalbumin.