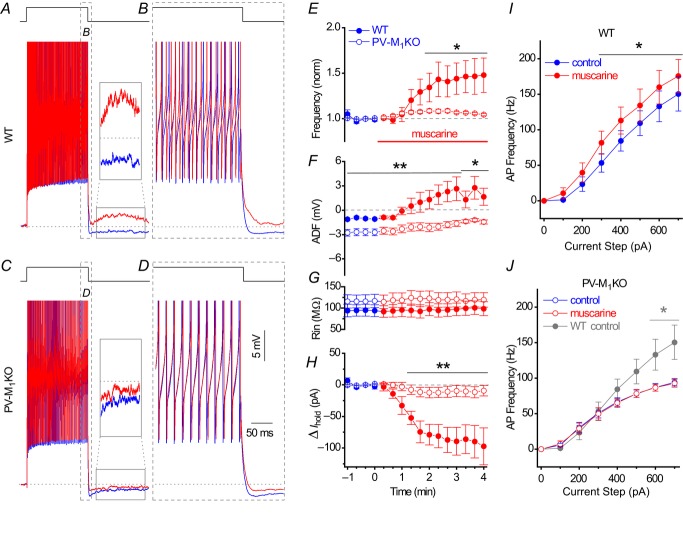
Figure 8. M1 mAChRs control the cellular excitability of hippocampal CA1 PV cells.
A, whole cell voltage responses to the introduction of a 1 s long 500 pA current step from −60 mV in a representative PV cell under (blue) control and (red) 10 μm muscarine conditions (APs truncated for display). Inset, solid box expanded to illustrate the conversion of the afterhyperpolarization to an afterdepolarization (dotted line indicates −60 mV baseline). B, expanded region in (A) displaying mAChR-induced changes during offset of the 500 pA current step. C and D, corresponding voltage responses observed in a PV cell from a PV-M1KO mouse, illustrating that mAChR activation neither increased AP frequency nor converted the afterhyperpolarization to an afterdepolarization. Population data from PV cells summarizing the time course of (E) change in AP frequency (normalized to the average AP frequency in a 1 min region before wash-in of muscarine), (F) ADF, (G) Rin and (H) relative change in Ihold from (blue) control to (red; at time 0) muscarine conditions. * and ** indicate times where significant differences (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01, respectively) were detected between WT (closed symbols, n = 8) and PV-M1KO mice (open symbols, n = 9) in (E–G) (Mann–Whitney test). Input–output relationships between AP frequency and current step magnitude (100–700 pA) for WT (I; n = 6) and PV-M1KO mice (J; open circles, n = 8). *P < 0.05 for 300–700 pA in WT (paired t test, n = 6) but not in PV-M1KO mice (paired t test, P > 0.05, n = 8). Control (blue) and muscarine (red) conditions are indicated. * in I denotes P < 0.05 between control conditions in (grey) WT and (blue) PV-M1KO mice (unpaired t test, P < 0.05 for 600–700 pA). PV cells were visualized with a floxed YFP AAV in both WT and PV-M1KO mice. ADF, afterdeflection; AP, action potential; M1KO, M1 mAChR knockout; mAChR, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; PV, parvalbumin; WT, wild-type.