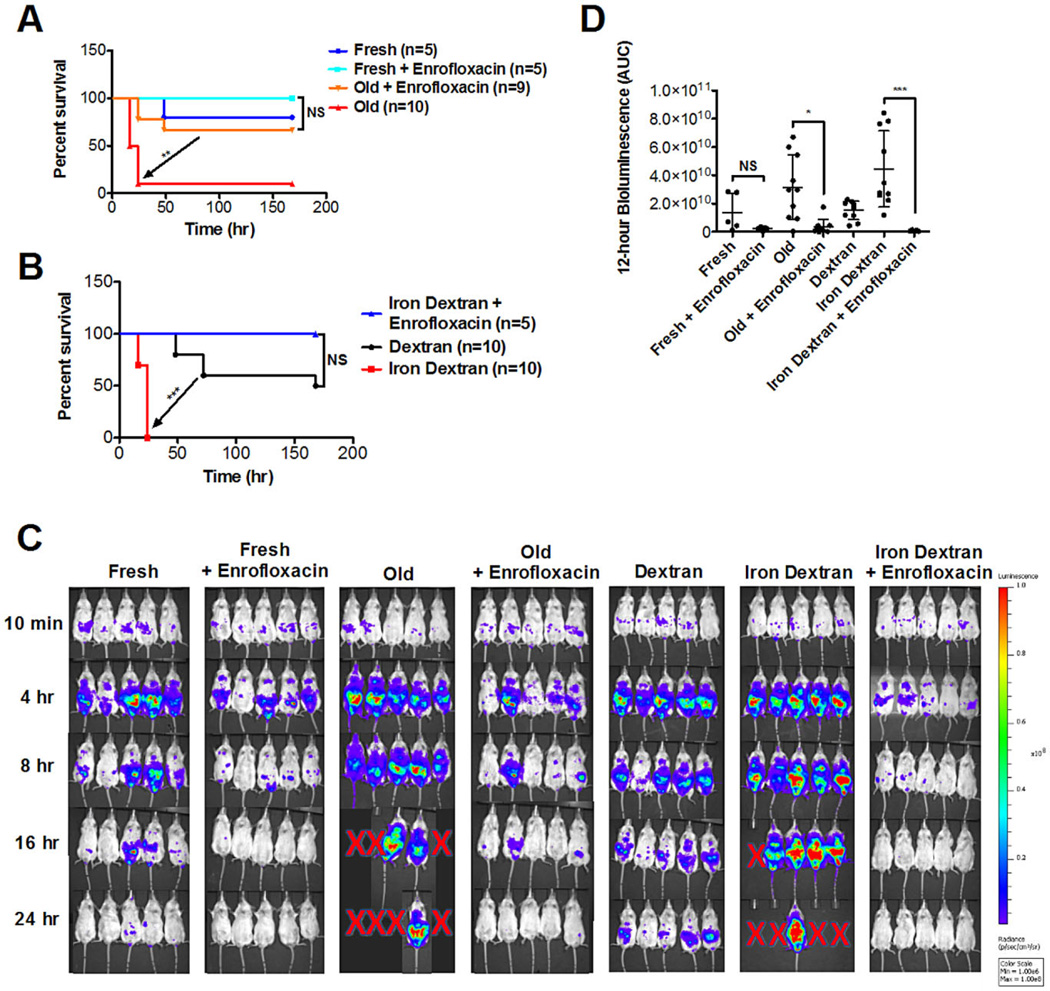
Fig. 4.
The effect of old RBC transfusions on exacerbating infection is ameliorated by antibiotic treatment. Experiments were performed using CD-1 mice, treated with or without a fluoroquinolone antibiotic (i.e., enrofloxacin). (A) Mice were transfused with syngeneic fresh RBCs (<24-hr storage) or old RBCs (2 weeks of storage) and concurrently infected intraperitoneally with E. coli strain Xen 14 (approx. 1 × 108 CFUs). Kaplan-Meier survival estimates are shown. (B) Mice were infused with dextran (20 mg; 70,000 MW) or iron dextran (0.5 mg iron) and concurrently infected intraperitoneally with E. coli strain Xen 14 (approx. 1 × 108 CFUs). Kaplan-Meier survival estimates are shown. (C) Representative bioluminescence images of mice at defined time points after infection, as described above. Red X’s represent animal death. (D) Bioluminescence was quantified in a defined region over the abdomen of each mouse and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for the first 12 hours (i.e., before animal dropout due to death or euthanasia for severe morbidity). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, as indicated.