Fig. 1.
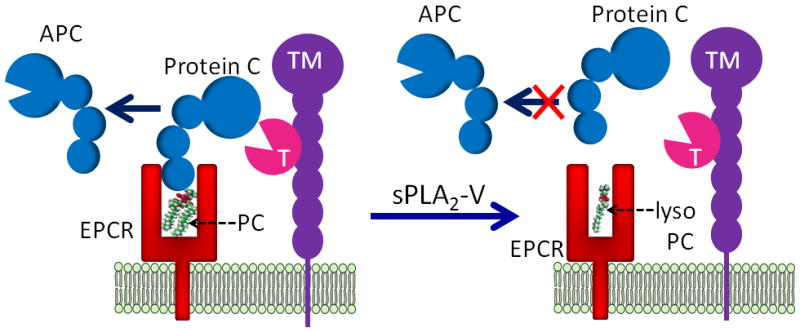
A hypothetical model of sPLA2-V impairment of protein C activation. Functional EPCR contains a phosphatidylcholine (PC) in its hydrophobic groove. In this conformation, EPCR can bind protein C. Thrombin (T):thrombomodulin (TM) complex activates the protein C bound to EPCR to generate activated protein C (APC). Secreted phospholipase A2, group V (sPLA2-V) hydrolyses the PC in the EPCR to lyso PC. The lipid modification in the hydrophobic groove of EPCR leads to a structural rearrangement in the helical region of EPCR, which probably results in narrowing of the pocket of the ligand-binding groove. The structurally rearranged EPCR is unable to bind protein C. The loss of protein C binding to EPCR translates into impaired protein C activation by thrombin:thrombomodulin complex.
