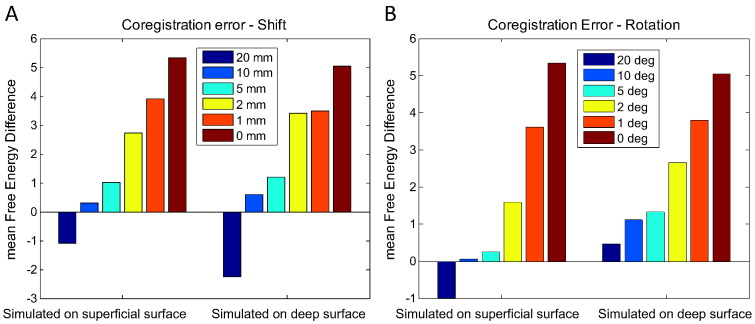
Fig. 3.
A: The effect of lateral coregistration error (shift). The bars shows the average (over triplet simulations) free energy difference between true and incorrect surface models (evidence in favour of the true model is positive) for source triplets simulated on the superficial (left) and deep (right) surface models. Different coloured bars show different levels of co-registration error in mm. Both plots indicate that the ability to discriminate between models representing different cortical surfaces is destroyed once coregistration error exceeds 2 mm (free energy differences < 3).
B: The effect of rotational coregistration error. The bars shows the average (over triplet simulations) free energy difference between true and incorrect surface models (evidence in favour of the true model is positive) for source triplets simulated on the superficial (left) and deep (right) surface models. Both for simulations based on the superficial as well as the deep surface model, the cut-off for being able to distinguish between the true/incorrect surface models (with 95% certainty or free energy > 3.0) lies around the 2-degree-mark.