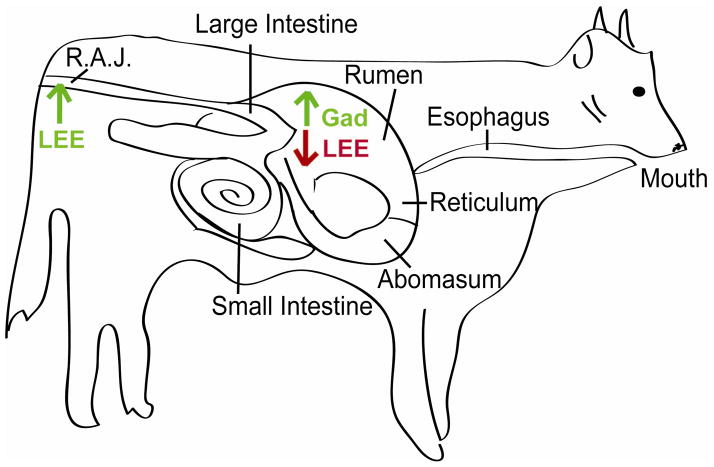
Figure 3.
Model of SdiA-AHL dependent EHEC gene expression in the GI of cattle. Once EHEC enters the rumen, it encounters AHLs. In the presence of AHLs, SdiA is functionally stable and acts to increase expression of acid-tolerance genes in the gad operon and represses expression of the LEE genes. Up-regulation of the gad genes allows EHEC to survive passage through the acidic abomasum. AHLs have not been detected in the colon, thus SdiA is unstable, and EHEC can activate the LEE and colonize the renal anal junction of the colon.