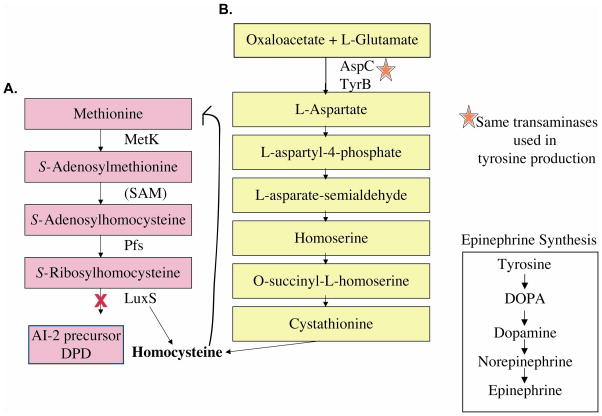
Figure 8.
Pathways for synthesis of homocysteine in E. coli. A. Methionine is important in the cell for production of the vital metabolic enzyme SAM (involved in the methylation of lipids, RNA, DNA, and protein) and de novo synthesis of methionine requires homocysteine. B. The luxS mutant cannot produce homocysteine through SRH hydrolysis; therefore, the oxaloacetate/L-glutamate pathway must be used. Oxaloacetate, L-glutamate, and the AspC and TyrB transaminases are used to produce aspartate, which than can proceed through a series of reactions, that result in the synthesis of homocysteine. Exclusive use of this pathway may lead to altered metabolism and amino acid content in the luxS mutant, leading to reduced AI-3 synthesis.