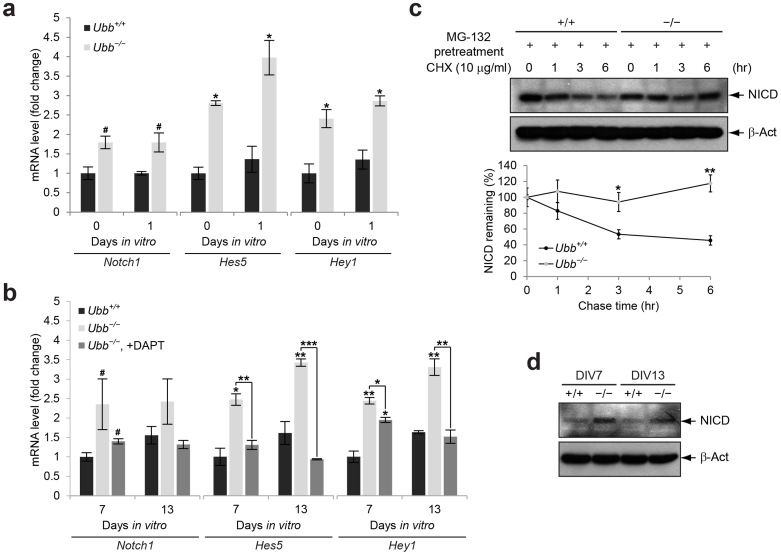
Figure 4. Upregulation of Notch target genes and increased steady-state levels of NICD in Ubb−/− cells.
(a) Notch1, Hes5, and Hey1 mRNA levels in cells isolated from wild-type (Ubb+/+) and Ubb−/− embryonic brains (n = 3 each) on 14.5 dpc (DIV0) or cultured in vitro for 1 day (DIV1) were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to Gapdh levels. mRNA levels are expressed as a fold increase relative to wild-type levels on DIV0. (b) Expression levels of Notch and its target genes in wild-type (Ubb+/+) and Ubb−/− cells (n = 3 each) on DIV7 and DIV13 were determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to Gapdh levels. mRNA levels are expressed as a fold increase relative to wild-type levels on DIV7. To repress Notch signaling, Ubb−/− cells cultured in vitro for 5 days (DIV5) were treated with 10 μM DAPT and cultured for another 2 to 8 days (DIV7 and DIV13). One-half of the medium containing 10 μM DAPT was changed every other day. (c) Cycloheximide (CHX) chase of stabilized NICD. Cells isolated from wild-type (+/+) and Ubb−/− (−/−) embryonic brains (n = 3 each) on 14.5 dpc and cultured in vitro for 7 days (DIV7) were pre-treated with 10 μM MG-132 for 2 hr to prevent degradation of NICD. Upon removal of MG-132, accumulated NICD was chased in medium containing 10 μg/ml CHX for up to 6 hr. β-Actin (β-Act) was used as a loading control. (d) Immunoblot detection of cleaved NICD in cells isolated from wild-type (+/+) and Ubb−/− (−/−) embryonic brains on 14.5 dpc and cultured in vitro for 7 and 13 days (DIV7 and DIV13). Representative immunoblot results of cells from three different embryonic brains per genotype are shown (c, d), and data are expressed as the means ± SEM from the indicated number of samples (a–c). #P < 0.1; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. Ubb+/+ on each day or as indicated by bars.