Figure 1.
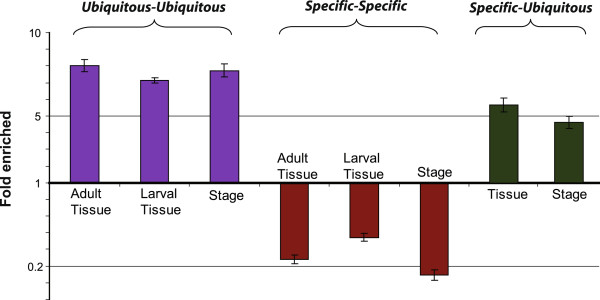
Ubiquitous proteins frequently interact with each other while tissue- and stage- specific proteins interact with ubiquitous proteins more frequently than with each other. For each set of proteins the number of interactions within the set (ubiquitous-ubiquitous and specific-specific) or between sets (ubiquitous-specific) was compared to the number of interactions in each of 5000 random protein sets taken from the composite PPI network. Each bar shows average fold-difference for 5000 trials. Standard deviations are shown as error bars. The p-value significance for each case is <7.56 × 10-5 at a CI = 99.99%. Ubiquitous-ubiquitous interactions were tested with adult tissue-ubiquitous proteins, larval tissue-ubiquitous proteins, and stage-ubiquitous proteins. Specific-specific interactions were tested with adult tissue-specific proteins, larval tissue-specific proteins, and stage-specific proteins. Ubiquitous-specific interactions were tested between adult tissue-ubiquitous and tissue-specific proteins or between stage-ubiquitous and stage-specific proteins.
