Figure 1.
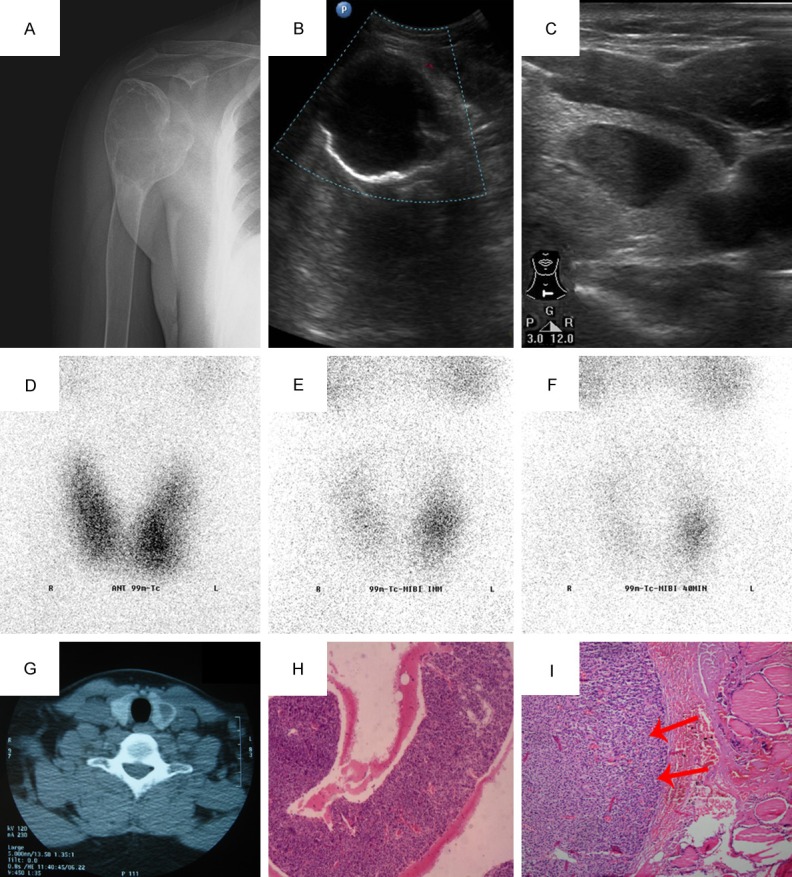
A. Round, radiolucent and osteolytic bone-expanding lesion was found in the right humeral head by X-ray; B. The ultrasound showed that there was a cystic mass in the right upper humeral shaft, which was irregular, well-demarcated and without any blood flow signals; C. Ultrasonography of neck showed there was a hypoechoic nodule (18 × 15 × 7 mm) inside the left lobe of his thyroid gland, which was of a standard shape, well-demarcated, homogeneous and a cystic area within; D. space-occupying effect can be seen in the thyroid static imaging; E&F. Dual-time point imaging showed the focal accumulation of radiotracer uptake in the left lower lobe thyroid; G. CT of the neck revealed a large low-density mass in the left lower lobe thyroid; H. Aspiration biopsy assumed that this intrathyroidal nodule was a ectopic parathyroid adenoma (HE, × 40); I. Ectopic parathyroid adenoma, chief cell type. The tumor cells had round or ovoid nuclei with densely stained chromatin. The tumor (left) was surrounded by a rim of normocellular thyroid gland (HE, × 100).
